How do scientists predict space weather?
Advanced Level Guiding Question
Big Idea 1.2Educator Background
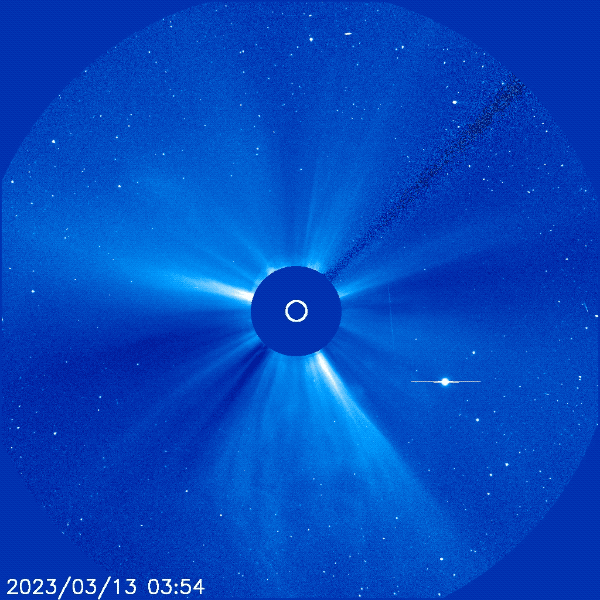
Scientists use a variety of methods to predict space weather. There are both ground-based observatories and satellites in Earth's orbit (and in orbit around the Sun) that take measurements that can help to predict space weather. Scientists predict space weather by monitoring the solar cycle (approximately 11 years), which can be observed by counting the number of sunspots, measuring changes in Earth's magnetic field, and by studying the Sun's atmosphere, the corona.
Learning Constraints
At this level students have a deeper understanding of electromagnetism (HS-PS2-4,5), can quantify field interactions with Coulomb's Law (HS-PS2-4), and explain how Earth is able to generate a magnetic field, due to a rotating liquid outer core of Earth (HS-ESS2-3).
Connect to Heliophysics
Connect to the Sun by focusing on the magnetic interactions on the Sun, including magnetic reconnection, and how the Sun's magnetic fields interact with Earth's magnetic field. Scientists use the Kp-Index to quantify the level of disturbance in Earth's magnetic field in order to predict space weather. Have students compare their analysis of sunspot data to their analysis of data from Earth-based magnetometers.
Extend Exploration
Extend student exploration by having students explore the Van Allen Radiation Belts, which are essentially particles from the solar wind caught in the Earth's magnetosphere.
Differentiate for Beginner Learners
Support beginner students by reviewing the basics of magnetic field interactions (MS-PS2-5).
Differentiate for More Advanced Learners
Challenge students at the next level to investigate how technologies are impacted. For example, changes in Earth magnetic fields cause electrical currents to flow in the Earth’s crust. Sometimes these currents can find their way into transformers, causing the transformers to overheat and fail, resulting in electrical blackouts.

Featured Advanced Resources
Explore this guiding question with these featured advanced level resources.
Heliophysics Resource Database
Use the guiding question above to explore resources at this level or go directly to our database to search for resources by level, NGSS performance expectation, topic, and mission.
Resource Database