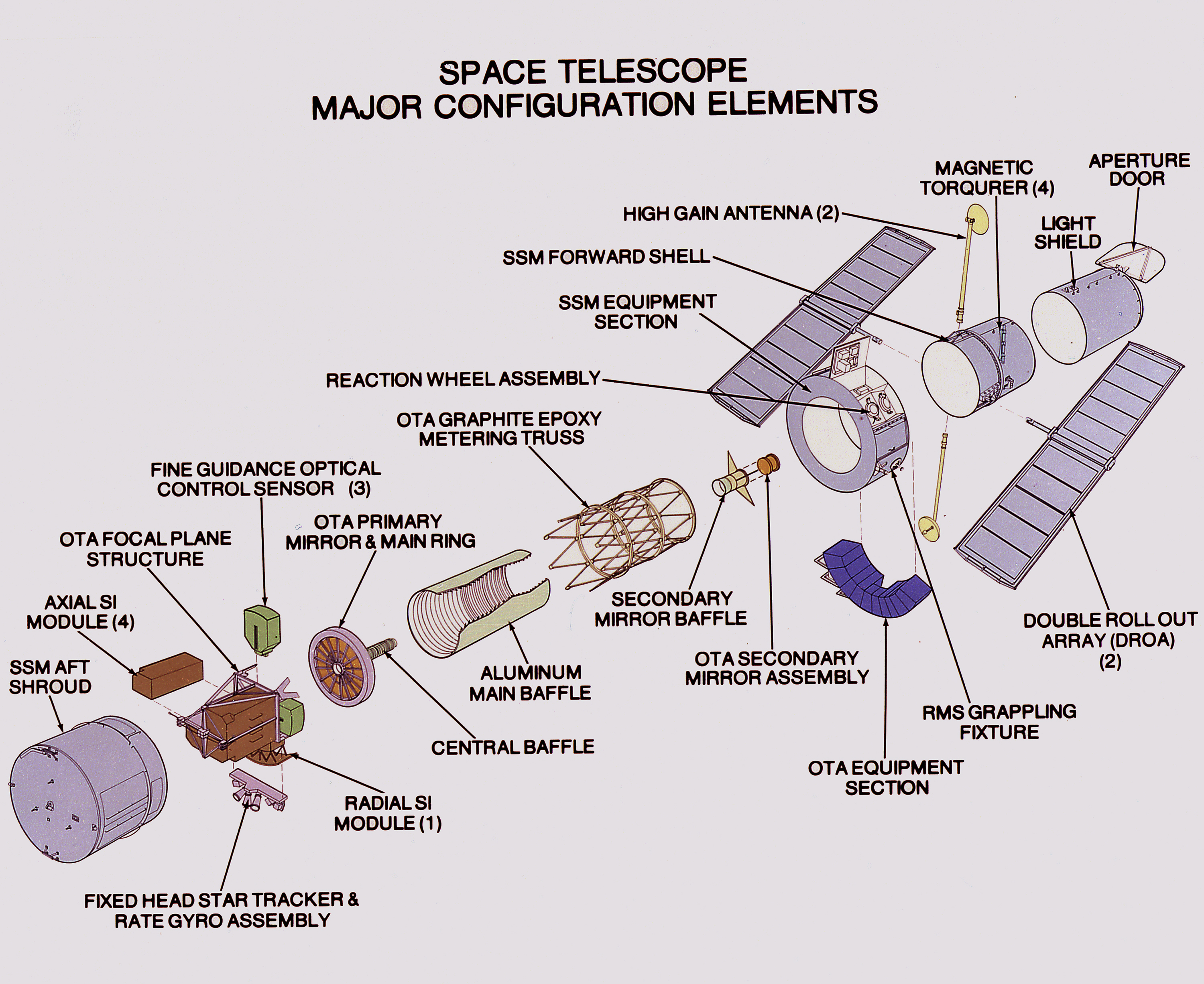
HST Major Configuration Elements
This illustration shows the Hubble Space Telescope's major configuration elements. The spacecraft has three interacting systems: the Support System Module (SSM), an outer structure that houses the other systems and provides services such as power, communication, and control; the Optical Telescope Assembly (OTA), which collects and concentrates the incoming light in the focal plane for use by the Scientific Instruments (SI); and five SIs. The SI Control and Data Handling (CDH) unit controls the five SIs, four that are housed in an aft section focal plane structure and one that is placed along the circumference of the spacecraft. The purpose of Hubble, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of Earth's atmosphere. Hubble detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than is visible from ground-based telescopes, extending our view more than 13 billion light-years away. Hubble views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, planet formation in other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. The Marshall Space Flight Center was responsible for the design, development, and construction of the observatory. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation in Danbury, Connecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors. The Lockheed Missile and Space Company of Sunnyvale, California, produced the protective outer shroud and spacecraft systems, and assembled and tested the finished telescope.
