Callisto: Exploration
Callisto and Jupiter’s three other largest moons were discovered in 1610 by Italian scientist Galileo Galilei.
Almost 400 years later, a spacecraft bearing his name—the Galileo orbiter—began the first in depth study of the Jovian system, including Callisto and its sister moons. Galileo orbited Jupiter until the mission ended in 2003.
Since then, several NASA spacecraft, including Cassini and New Horizons, have studied the moon, taking images of its surface and gathering other data.
Xianzhe Jia
Scientist - NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL)
"Cassini is such a fantastic mission. It not only acquired a wealth of data that led to numerous discoveries, but also raised a new generation of planetary scientists, including myself."
More about Xianzhe Jia
Suzanne "Suzy" Dodd
Project Manager - Jet Propulsion Laboratory
"Math is going to be the basis for all the science and engineering that you will have to do in the future."
More about Suzanne "Suzy" Dodd
Margaret Kivelson
Scientist
Remember, I started before there were any spacecraft!
More about Margaret Kivelson
Joan Salute
Program Executive - NASA Headquarters
Don't be afraid to try new areas. I was in the Earth sciences remote sensing area for 15 years before venturing out.
More about Joan Salute
Active
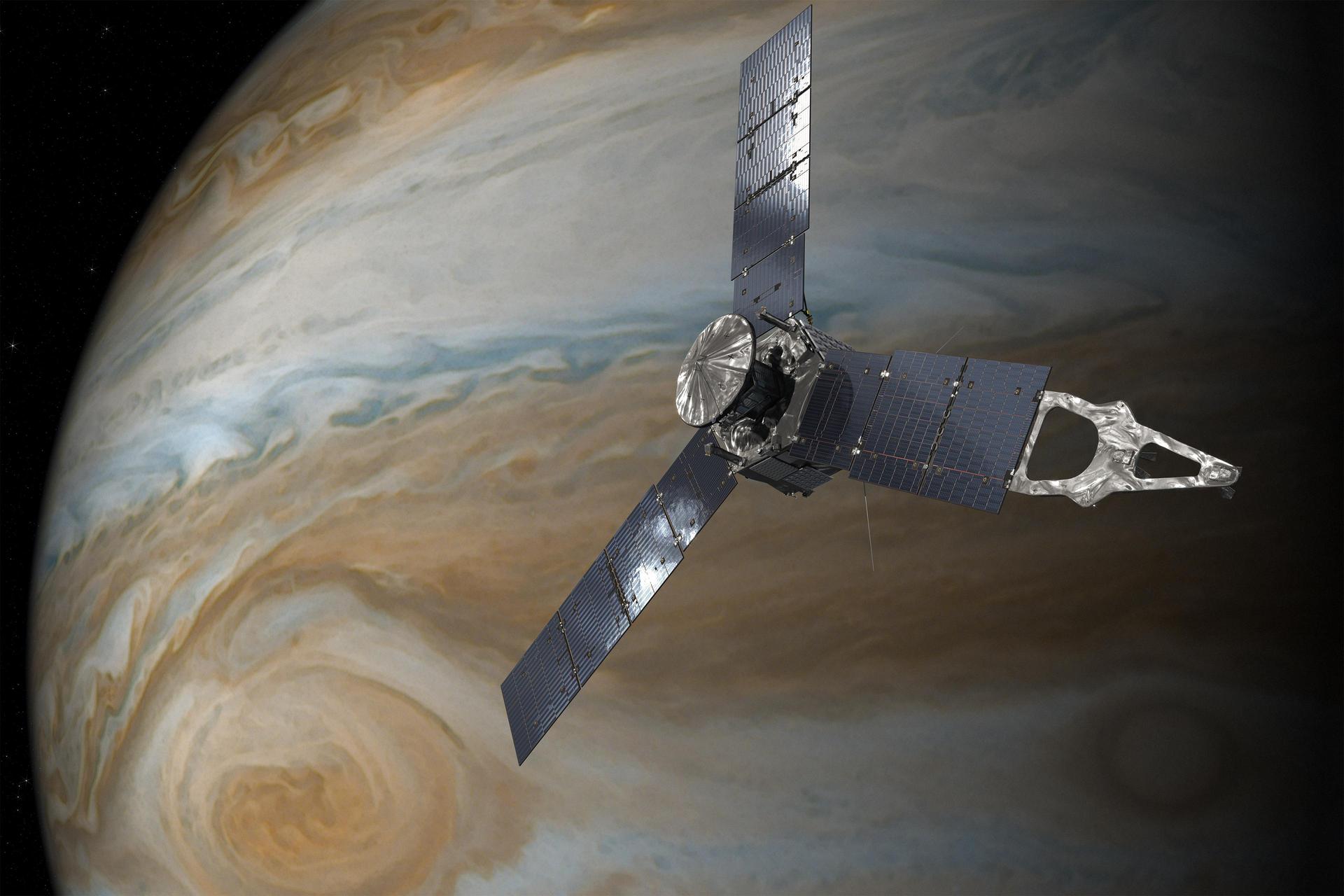

Juno
Launch Date: August 5, 2011. Juno is on a mission to probe beneath Jupiter's dense clouds and answer questions about the origin and evolution of Jupiter, and our solar system.
Hubble Space Telescope
Launch Date: April 24, 1990. The Hubble Space Telescope was designed to provide clear and deep views of distant galaxies and stars and most of the planets in our solar system.

Voyager 1
Launch Date: September 5, 1977. Voyager 1 successfully flew by both the Jupiter and Saturn systems before continuing out into the farthest most reaches of our solar system.
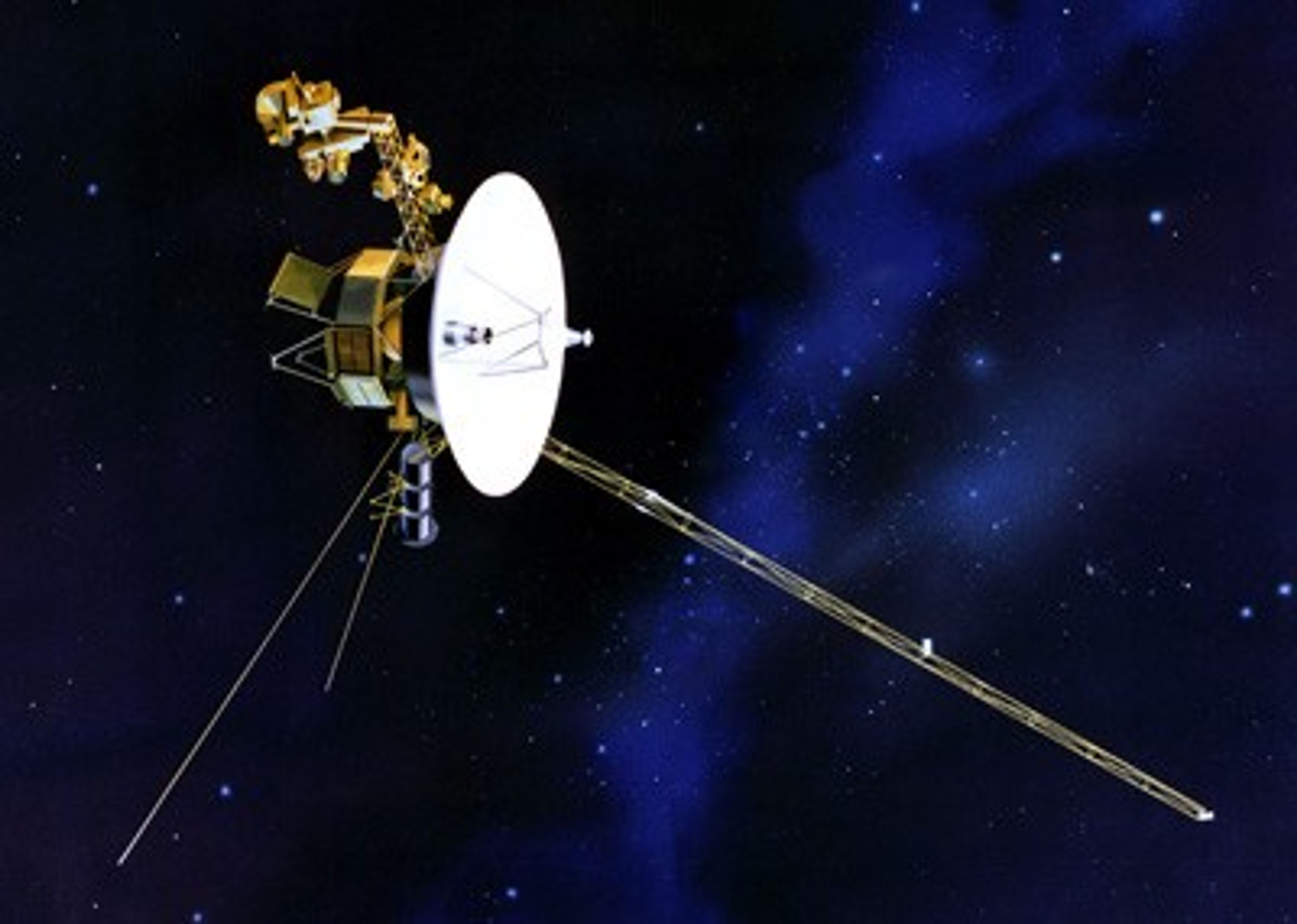

Voyager 2
Launch Date: August 20, 1977. Voyager 2 is the only spacecraft to study all four of the solar system's giant planets at close range.
Past

Ulysses
Launch Date: October 6, 1990. Ulysses was the first spacecraft to explore the Sun from a unique polar orbit.

Galileo
Launch Date: October 18, 1989. Galileo was designed to make the first study of Jupiter and its moons and magnetosphere from orbit. The orbiter carried 10 science instruments and a atmospheric probe.
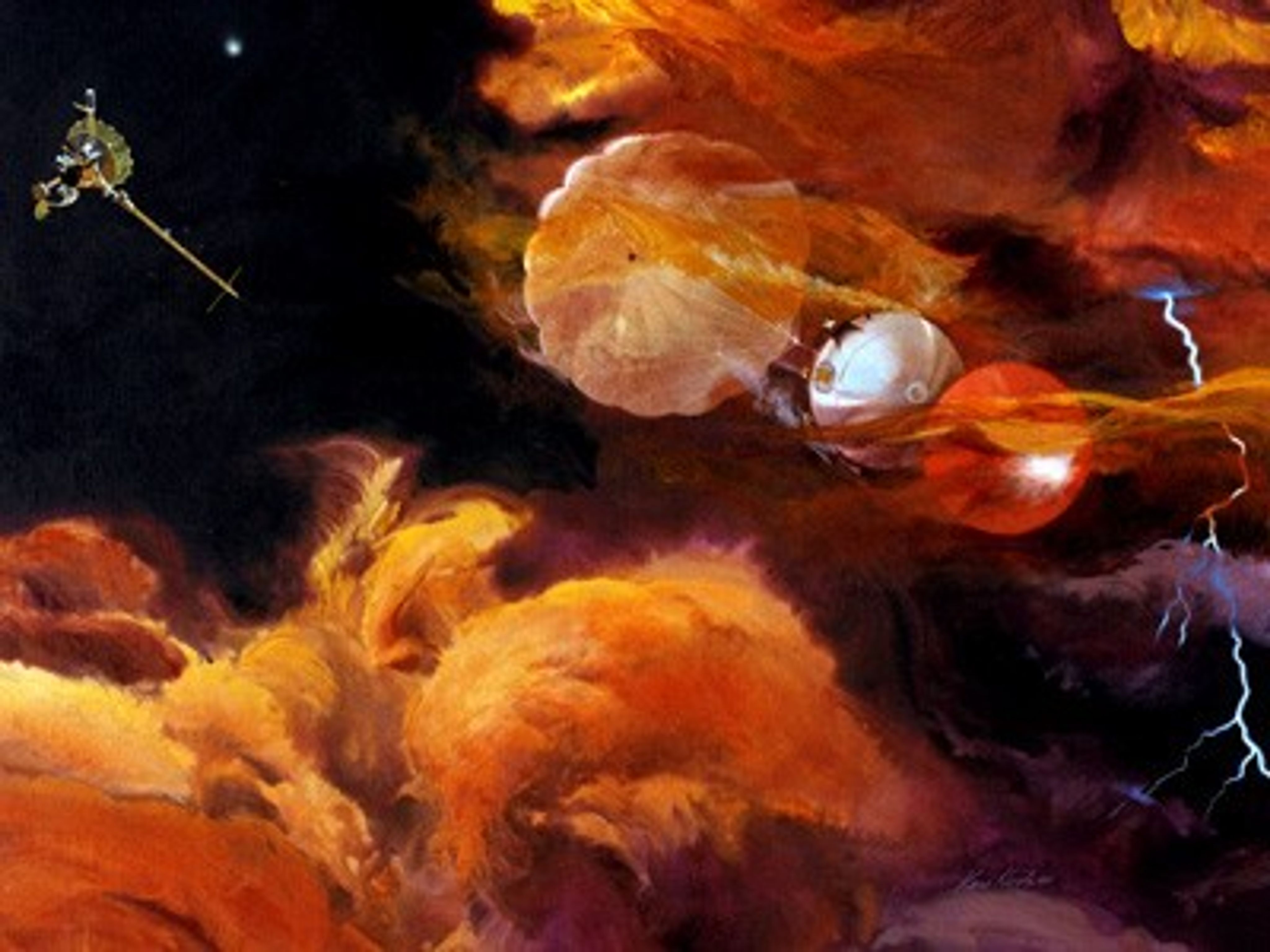

Galileo Jupiter Atmospheric Probe
Launch Date: October 18, 1989. The Galileo spacecraft and probe traveled as one for almost six years. In July 1995, the probe was released to begin a solo flight into Jupiter

Pioneer 10
Launch Date: March 3, 1972. Pioneer 10, the first NASA mission to the outer planets, was the first spacecraft placed on a trajectory to escape the solar system into interstellar space; first to fly beyond Mars; first to fly through the asteroid belt; first to fly past Jupiter; first to use all-nuclear electrical power, and the first human-made object to fly beyond Neptune.
The first thing that fired my imagination for planetary science was when the NASA Voyager spacecraft discovered active volcanoes on Jupiter's moon Io.

Ashley Davies
Volcanologist
The important thing about being a scientist or an engineer is learning how to think critically, learning how to be creative, learning problem solving and learning how to learn.

Tracy Drain
Flight Systems Engineer
Eyes on the Solar System
Eyes on the Solar System lets you explore the planets, their moons, asteroids, comets and the spacecraft exploring them from 1950 to 2050. Ride with the Curiosity Rover as it lands on Mars or fly by Pluto with the New Horizons spacecraft all from the comfort of your home computer.
Learn More