Messier 17
Messier 17 is better known as the Omega Nebula or Swan Nebula.
Distance
5,500 light-years
Apparent Magnitude
6.0
constellation
Sagittarius
object type
Emission Nebula
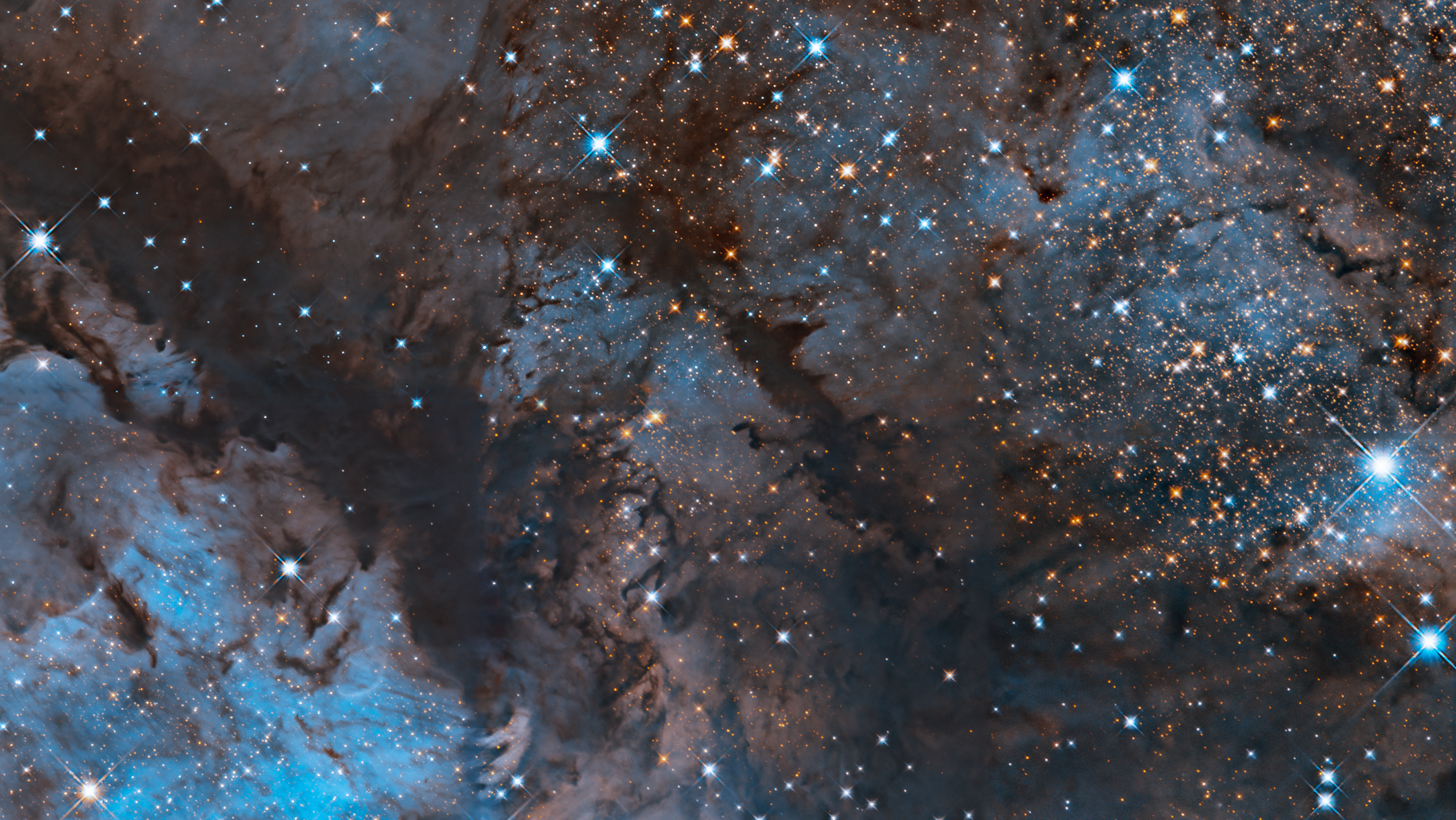

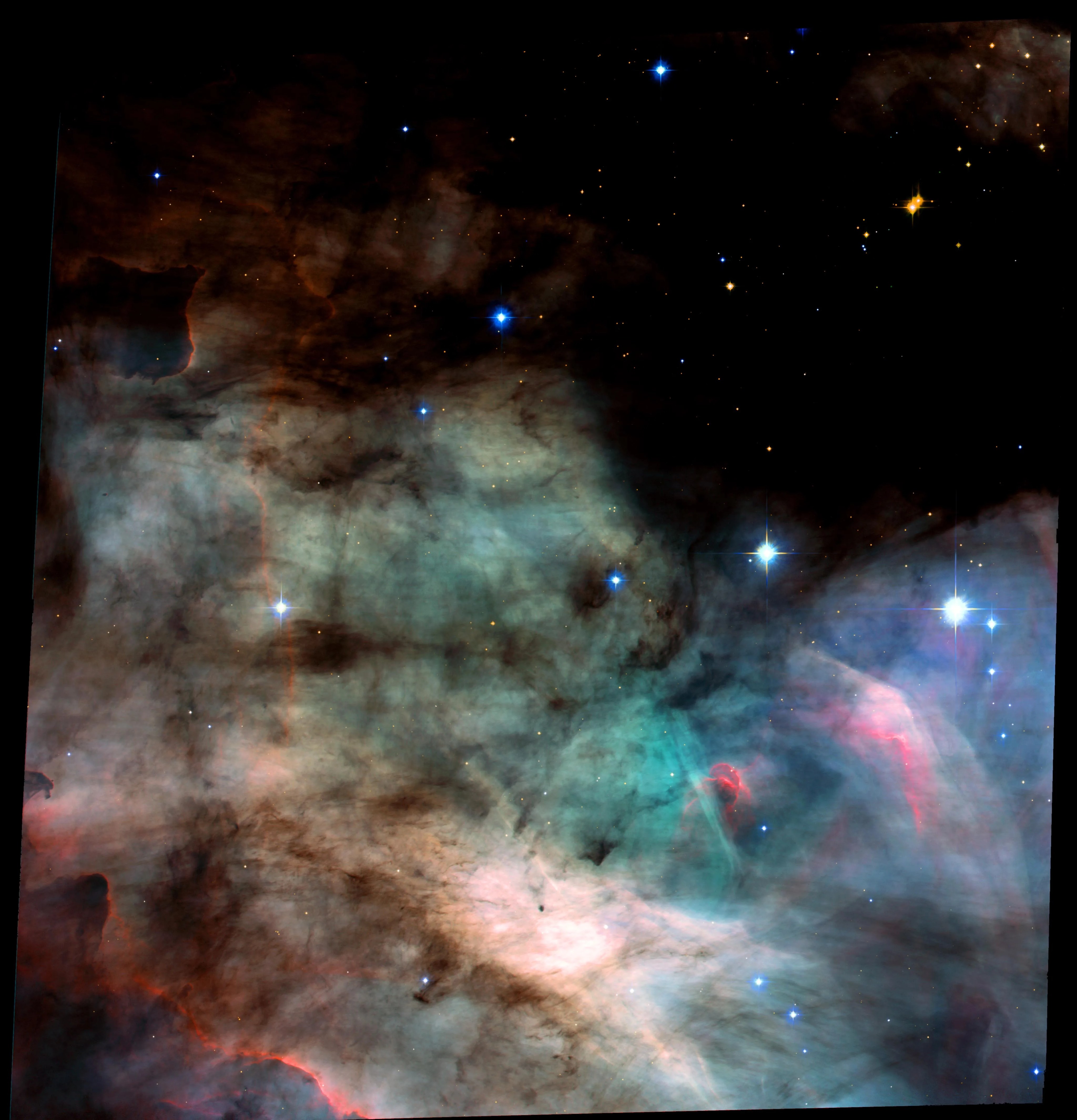
M17, also known as the Omega Nebula or Swan Nebula, is one of the largest star-forming regions in the Milky Way galaxy. Hubble’s stunning image of a central portion of the nebula has been colorized to highlight certain wavelengths of light. Green represents oxygen while red reveals hydrogen and infrared light.
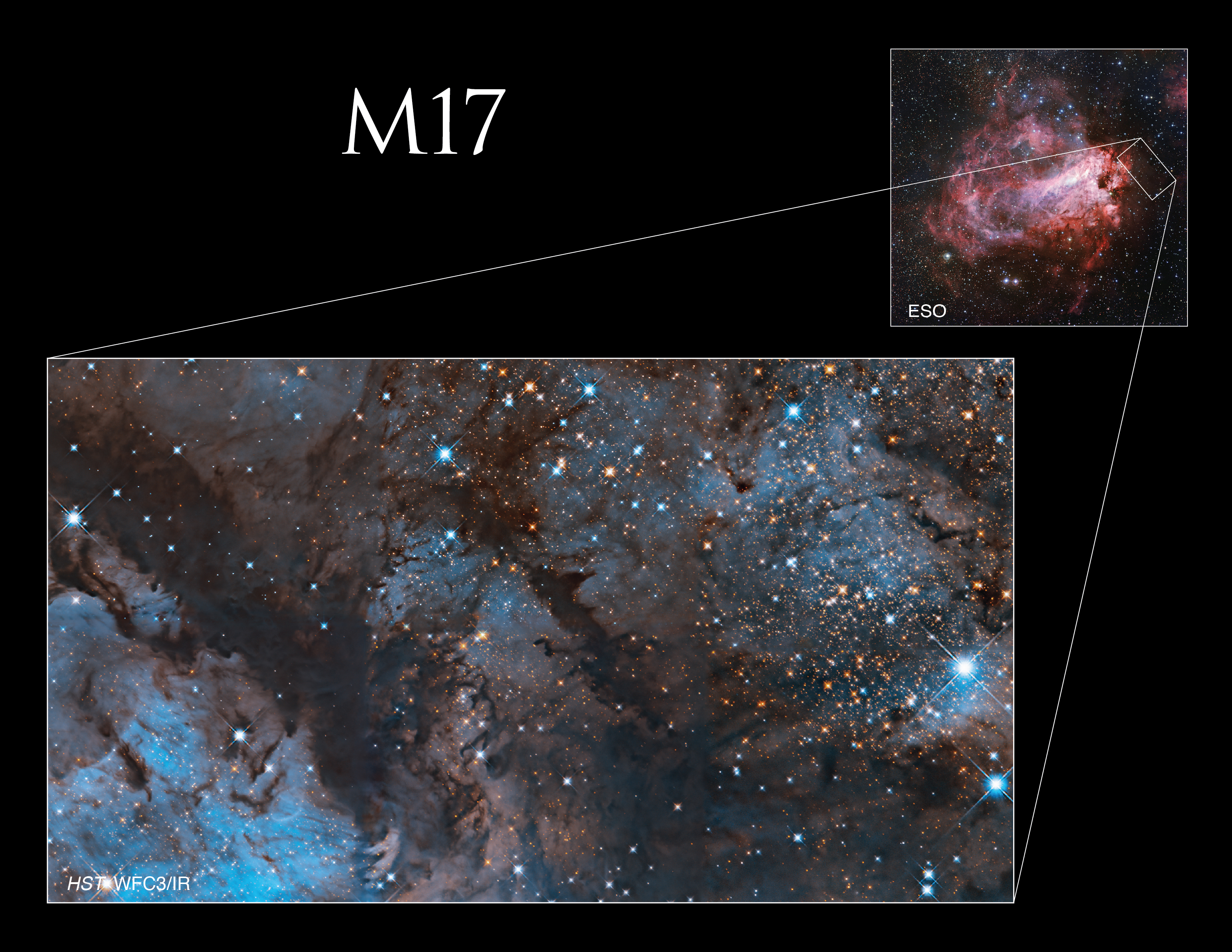
The Omega Nebula was discovered in 1745 by the Swiss astronomer Jean-Philippe Loys de Chéseaux. It is located 5,500 light-years from Earth in the constellation Sagittarius. The nebula has an apparent magnitude of 6 and can be seen with a pair of binoculars. M17, which appears near M16 and M18 in the sky, is best viewed on clear nights in August.
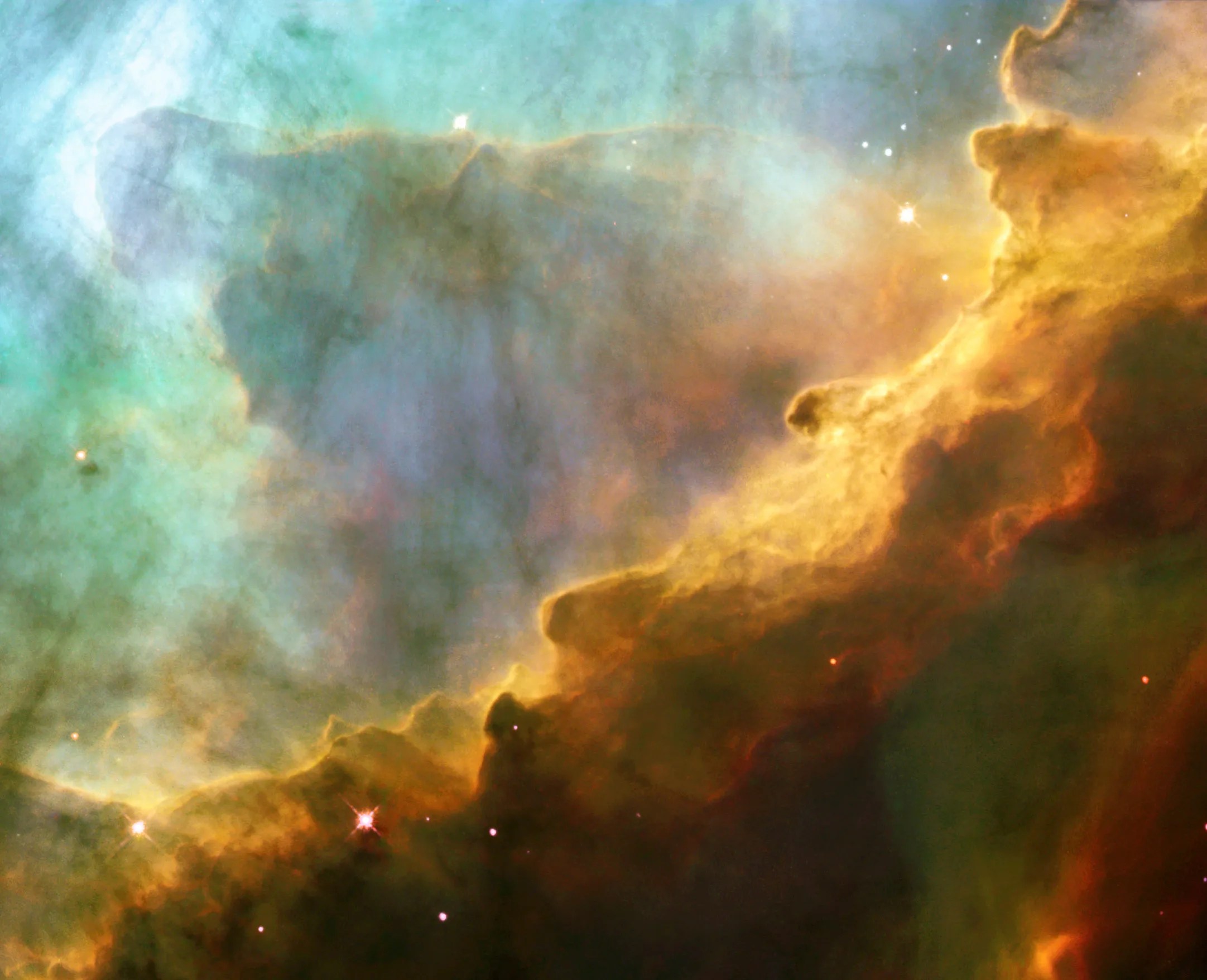

M17 contains one of our galaxy’s youngest star clusters, at only 1 million years old. However, many of the young stars in this cluster are impossible to see because of the gas and dust that surrounds them. The powerful radiation from the young stars evaporates and erodes the dense clouds of cold gas in which new stars form. One such pocket of gas is seen at the center of the brightest region of the nebula (near the bottom of this image) and is about 10 times larger than our solar system. Other dense pockets of gas have formed the remarkable dark features jutting inward from the bottom left corner of the image.

For more information about Hubble’s observations of M17, see:
Explore Hubble's Messier Catalog
The following pages contain some of Hubble’s best images of Messier objects.
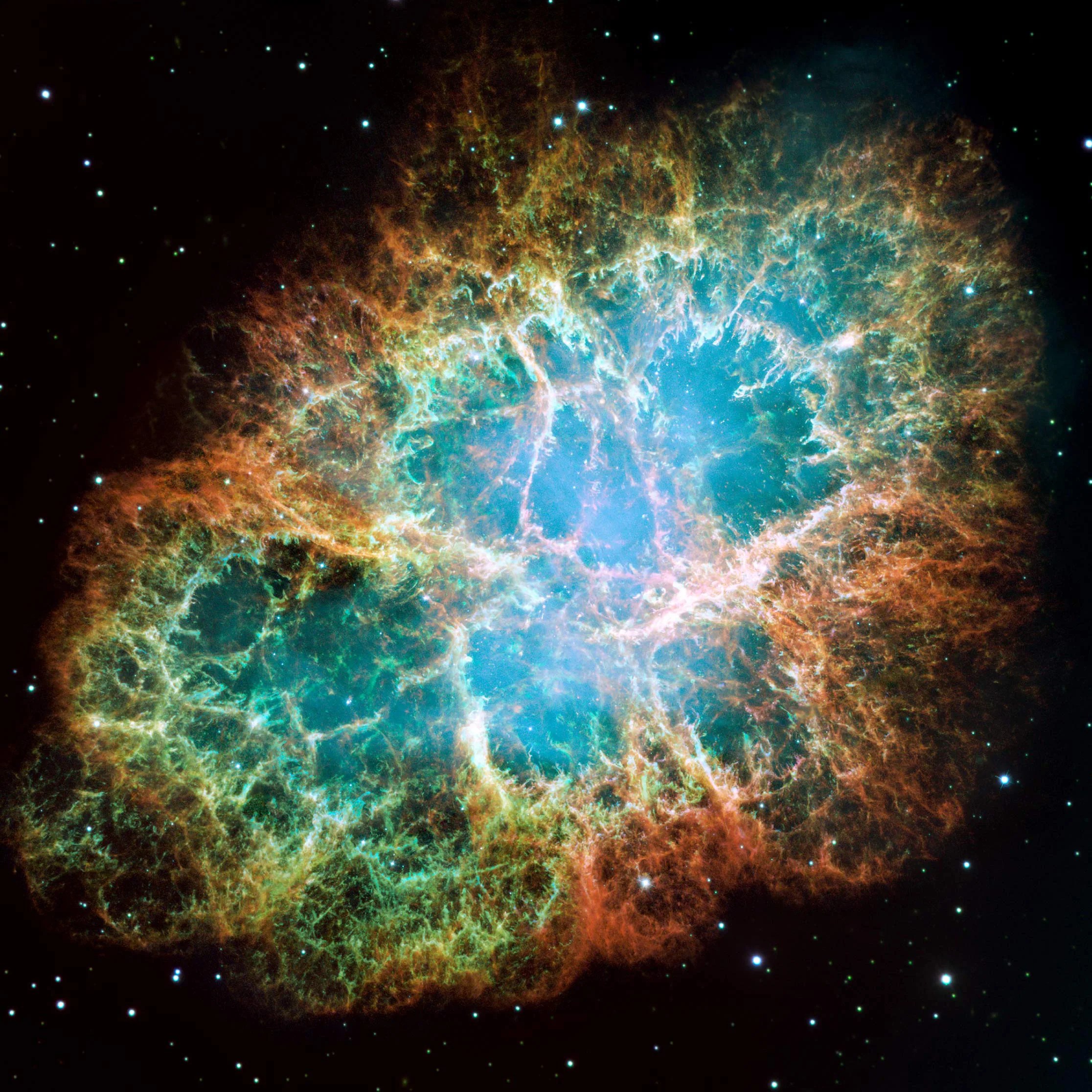

Messier 1 (The Crab Nebula)
Better known as the Crab Nebula, Charles Messier originally mistook Messier 1 for Halley’s Comet, which inspired him to create…
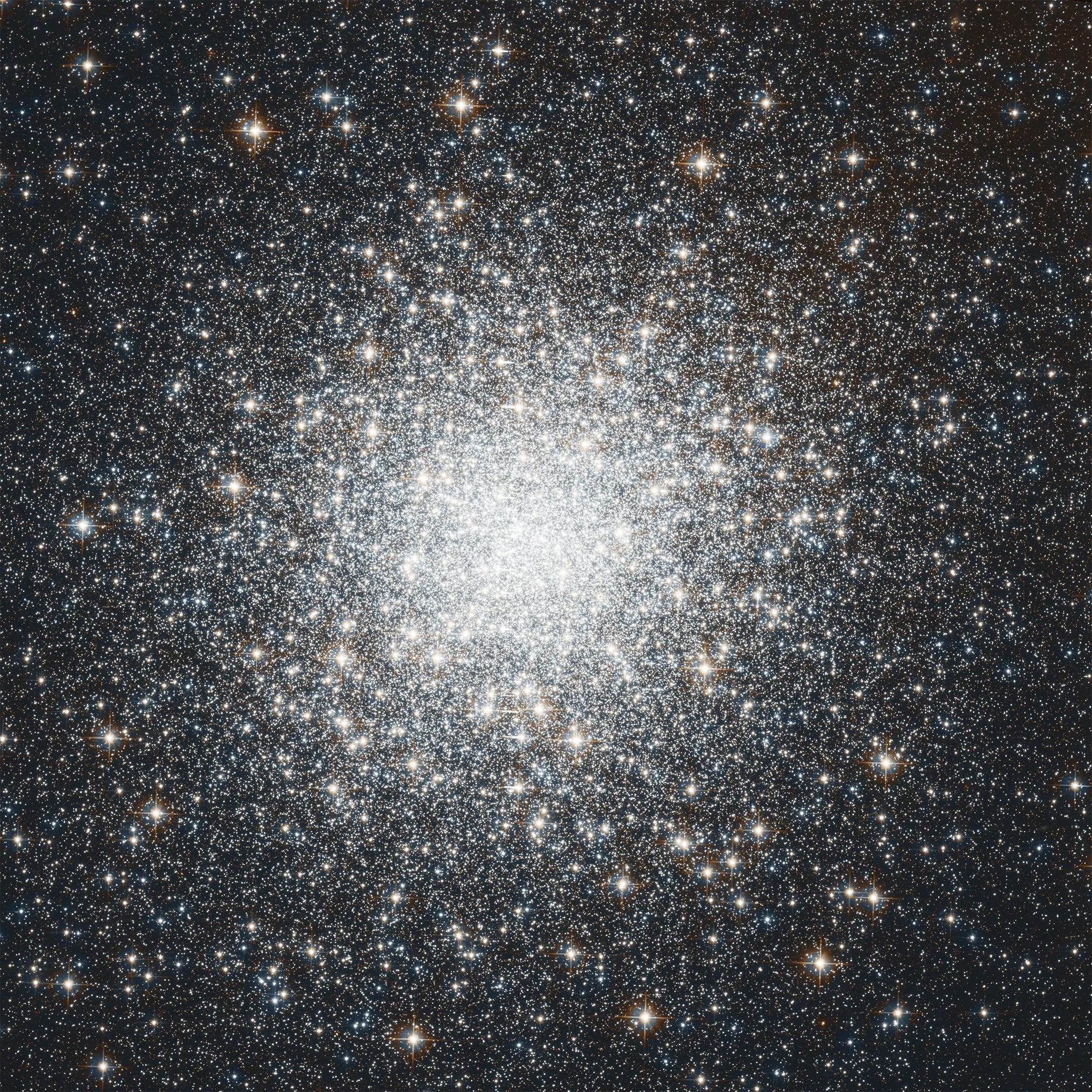

Messier 2
Hubble's image of Messier 2 is comprised of visible and infrared wavelengths of light.
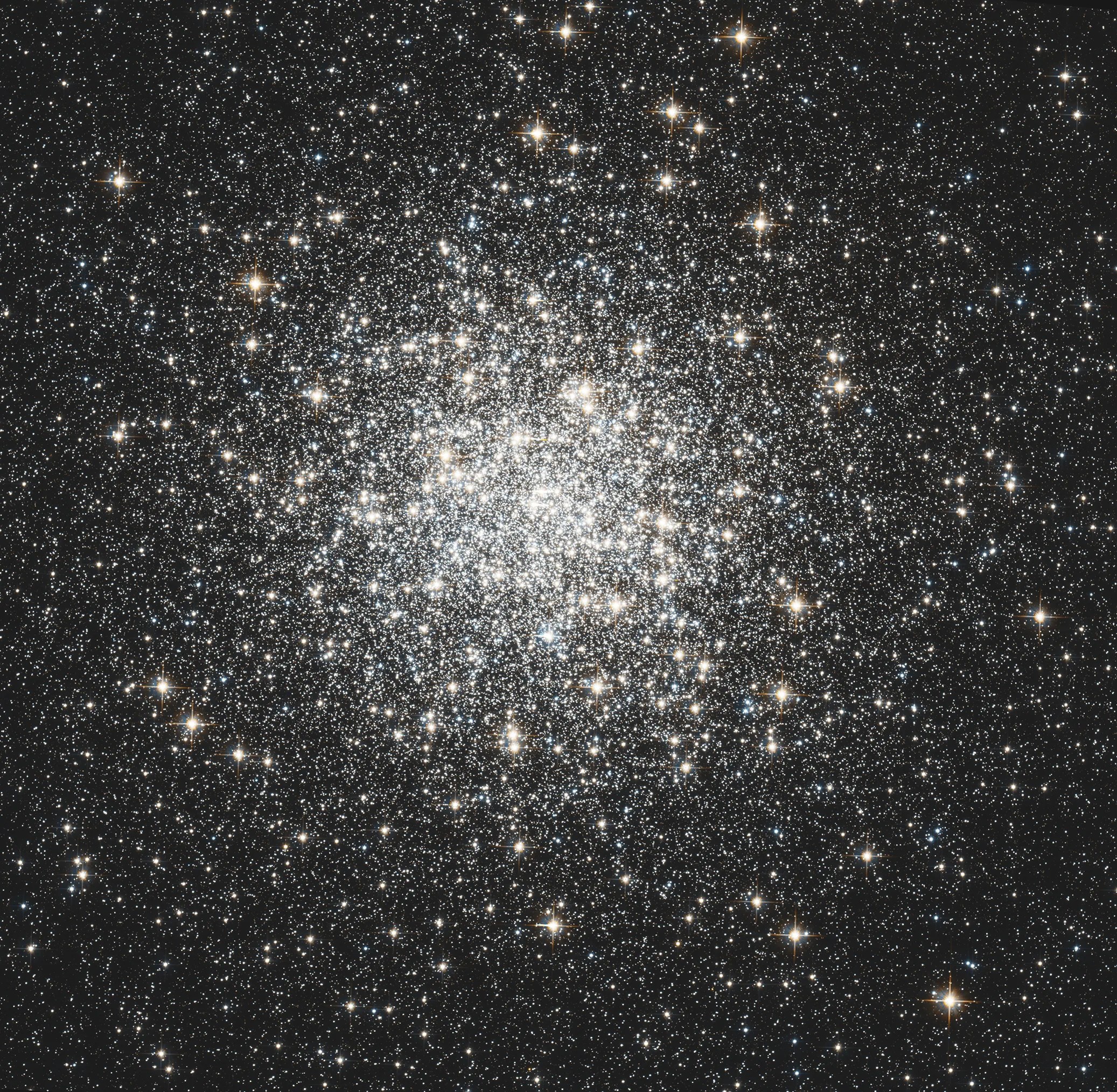

Messier 3
Messier 3 holds more than 500,000 stars.