

Webb Telescope Latest News
Webb's latest news releases in reverse chronological order going back to 2012.
Webb News Feed
Search and sort the news feed with the controls immediately below.

NASA’s Webb Finds Planet-Forming Disks Lived Longer in Early Universe
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope just solved a conundrum by proving a controversial finding made with the agency’s Hubble Space Telescope more than 20 years ago. In 2003, Hubble provided evidence of a massive planet around a very old star,…

NASA Successfully Integrates Roman Mission’s Telescope, Instruments
NASA’s Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope team has successfully integrated the mission’s telescope and two instruments onto the instrument carrier, marking the completion of the Roman payload. Now the team at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, will…

Found: First Actively Forming Galaxy as Lightweight as Young Milky Way
For the first time, NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has detected and “weighed” a galaxy that not only existed around 600 million years after the big bang, but is also similar to what our Milky Way galaxy’s mass might have…

Hats Off to NASA’s Webb: Sombrero Galaxy Dazzles in New Image
In a new image from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, a galaxy named for its resemblance to a broad-brimmed Mexican hat appears more like an archery target. In Webb’s mid-infrared view of the Sombrero galaxy, also known as Messier 104…

Astronomers Find Early Fast-Feeding Black Hole Using NASA Telescopes
A rapidly feeding black hole at the center of a dwarf galaxy in the early universe, shown in this artist’s concept, may hold important clues to the evolution of supermassive black holes in general. Using data from NASA’s James Webb…

NASA’s Hubble, Webb Probe Surprisingly Smooth Disk Around Vega
In the 1997 movie “Contact,” adapted from Carl Sagan’s 1985 novel, the lead character scientist Ellie Arroway (played by actor Jodi Foster) takes a space-alien-built wormhole ride to the star Vega. She emerges inside a snowstorm of debris encircling the…

‘Blood-Soaked’ Eyes: NASA’s Webb, Hubble Examine Galaxy Pair
Stare deeply at these galaxies. They appear as if blood is pumping through the top of a flesh-free face. The long, ghastly “stare” of their searing eye-like cores shines out into the supreme cosmic darkness. It’s good fortune that looks…

NASA’s Webb Reveals Unusual Jets of Volatile Gas from Icy Centaur 29P
Inspired by the half-human, half-horse creatures that are part of Ancient Greek mythology, the field of astronomy has its own kind of centaurs: distant objects orbiting the Sun between Jupiter and Neptune. NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has mapped the…

In Odd Galaxy, NASA’s Webb Finds Potential Missing Link to First Stars
Looking deep into the early universe with NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, astronomers have found something unprecedented: a galaxy with an odd light signature, which they attribute to its gas outshining its stars. Found approximately one billion years after the…

NASA’s Webb Provides Another Look Into Galactic Collisions
Smile for the camera! An interaction between an elliptical galaxy and a spiral galaxy, collectively known as Arp 107, seems to have given the spiral a happier outlook thanks to the two bright “eyes” and the wide semicircular “smile.” The…

NASA’s Webb Peers into the Extreme Outer Galaxy
Astronomers have directed NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope to examine the outskirts of our Milky Way galaxy. Scientists call this region the Extreme Outer Galaxy due to its location more than 58,000 light-years away from the Galactic Center. (For comparison,…

NASA’s Webb Reveals Distorted Galaxy Forming Cosmic Question Mark
It’s 7 billion years ago, and the universe’s heyday of star formation is beginning to slow. What might our Milky Way galaxy have looked like at that time? Astronomers using NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope have found clues in the…

Webb Finds Early Galaxies Weren’t Too Big for Their Britches After All
It got called the crisis in cosmology. But now astronomers can explain some surprising recent discoveries. When astronomers got their first glimpses of galaxies in the early universe from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, they were expecting to find galactic…

AstroViz: Iconic Pillars of Creation Star in NASA’s New 3D Visualization
NASA’s Universe of Learning – a partnership among the Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI), Caltech/IPAC, the Center for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian, and the Jet Propulsion Laboratory and part of the NASA Science Activation program portfolio – recently released…

How NASA’s Roman Space Telescope Will Illuminate Cosmic Dawn
Today, enormous stretches of space are crystal clear, but that wasn’t always the case. During its infancy, the universe was filled with a “fog” that made it opaque, cloaking the first stars and galaxies. NASA’s upcoming Nancy Grace Roman Space…

NASA’s Webb Images Cold Exoplanet 12 Light-Years Away
An international team of astronomers using NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has directly imaged an exoplanet roughly 12 light-years from Earth. The planet, Epsilon Indi Ab, is one of the coldest exoplanets observed to date. The planet is several times…

NASA’s Webb Investigates Eternal Sunrises, Sunsets on Distant World
Near-infrared spectral analysis of terminator confirms differences in morning and evening atmosphere Researchers using NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope have finally confirmed what models have previously predicted: An exoplanet has differences between its eternal morning and eternal evening atmosphere. WASP-39…

Vivid Portrait of Interacting Galaxies Marks Webb’s Second Anniversary
Two for two! A duo of interacting galaxies commemorates the second science anniversary of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, which takes constant observations, including images and highly detailed data known as spectra. Its operations have led to a “parade” of…

NASA’s Begoña Vila Awarded 2024 Galician Excellence Award
Begoña Vila, an instrument systems engineer from KBR who worked on NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, has been selected to receive the 2024 Galician Excellence Title in the Sciences and Medicine Category for her career and work on Webb. This award…

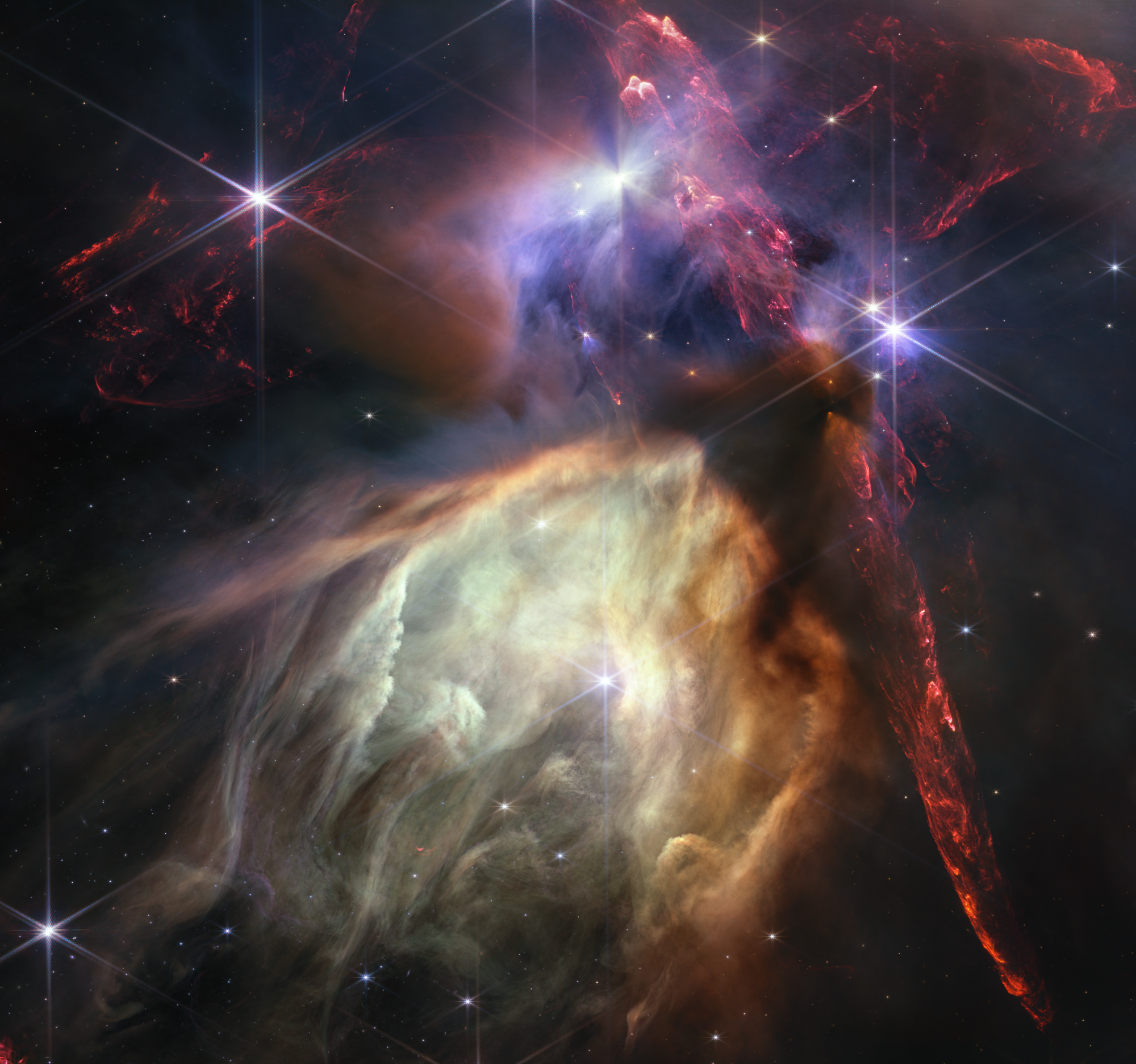
NASA’s Webb Captures Celestial Fireworks Around Forming Star
The colors within this mid-infrared image reveal details about the central protostar’s behavior. The cosmos seems to come alive with a crackling explosion of pyrotechnics in this new image from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope. Taken with Webb’s MIRI (Mid-Infrared…
What is Webb Observing?
See current, upcoming and recent past observations scientists are making with the Webb Space Telescope. View details about each observation's science focus areas, the instruments used and more.
View the Tool