4 min read
Like a sports photographer at an auto-racing event, NASA's Hubble Space Telescope captured a series of photos of asteroid Dimorphos when it was deliberately hit by a 1,200-pound NASA spacecraft called DART on September 26, 2022.

The primary objective of DART, which stands for Double Asteroid Redirection Test, was to test our ability to alter the asteroid's trajectory as it orbits its larger companion asteroid, Didymos. Though neither Didymos nor Dimorphos poses any threat to Earth, data from the mission will help inform researchers how to potentially divert an asteroid's path away from Earth, if ever necessary. The DART experiment also provided fresh insights into planetary collisions that may have been common in the early solar system.
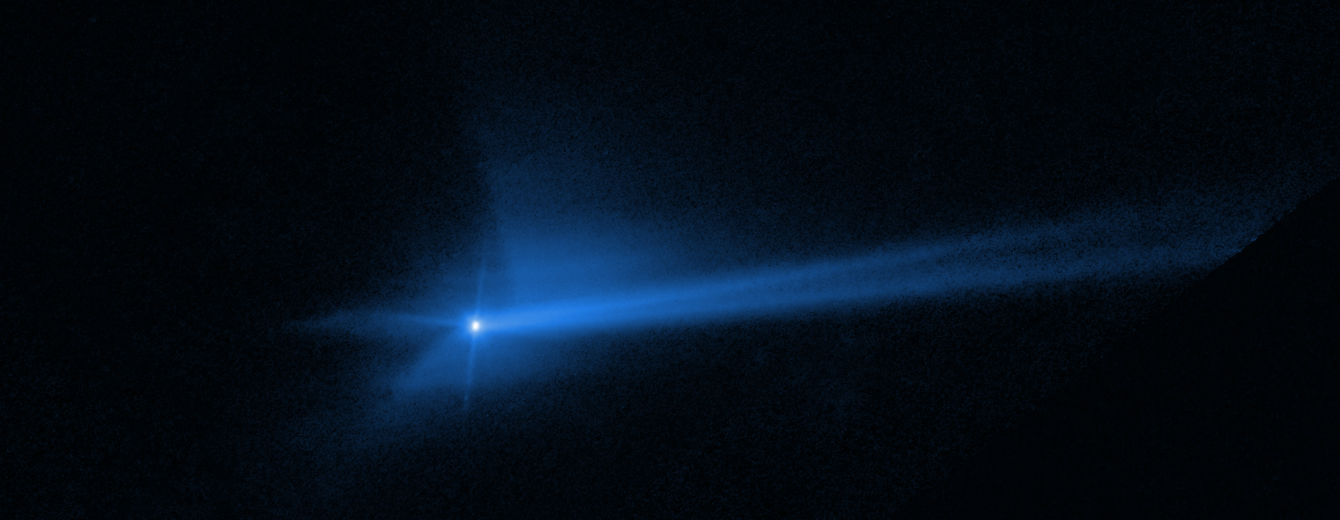
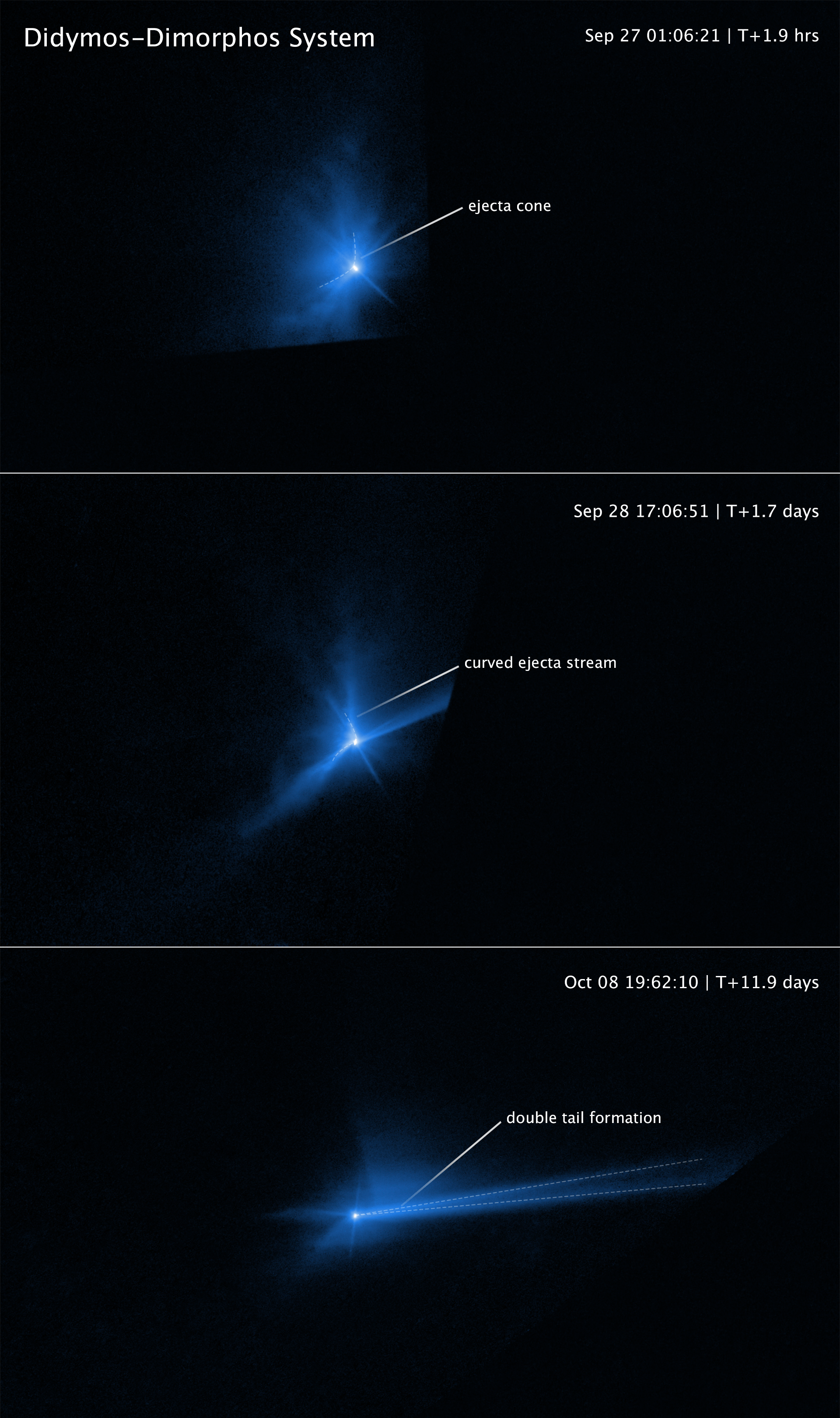
Hubble's time-lapse movie of the aftermath of DART's collision reveals surprising and remarkable, hour-by-hour changes as dust and chunks of debris were flung into space. Smashing head on into the asteroid at 13,000 miles per hour, the DART impactor blasted over 1,000 tons of dust and rock off of the asteroid.
The Hubble movie offers invaluable new clues into how the debris was dispersed into a complex pattern in the days following the impact. This was over a volume of space much larger than could be recorded by the LICIACube cubesat, which flew past the binary asteroid minutes after DART's impact.
"The DART impact happened in a binary asteroid system. We've never witnessed an object collide with an asteroid in a binary asteroid system before in real time, and it's really surprising. I think it's fantastic. Too much stuff is going on here. It's going to take some time to figure out," said Jian-Yang Li of the Planetary Science Institute in Tucson, Arizona. The study, led by Li along with 63 other DART team members, was published on March 1 in the journal Nature.
The movie shows three overlapping stages of the impact aftermath: the formation of an ejecta cone, the spiral swirl of debris caught up along the asteroid's orbit about its companion asteroid, and the tail swept behind the asteroid by the pressure of sunlight (resembling a windsock caught in a breeze).
The Hubble movie starts at 1.3 hours before impact. In this view both Didymos and Dimorphos are within the central bright spot; even Hubble can't resolve the two asteroids separately. The thin, straight spikes projecting away from the center (and seen in later images) are artifacts of Hubble's optics. The first post-impact snapshot is 2 hours after the event. Debris flies away from the asteroid, moving with a range of speeds faster than four miles per hour (fast enough to escape the asteroid's gravitational pull, so it does not fall back onto the asteroid). The ejecta forms a largely hollow cone with long, stringy filaments.
At about 17 hours after the impact the debris pattern entered a second stage. The dynamic interaction within the binary system starts to distort the cone shape of the ejecta pattern. The most prominent structures are rotating, pinwheel-shaped features. The pinwheel is tied to the gravitational pull of the companion asteroid, Didymos. "This is really unique for this particular incident," said Li. "When I first saw these images, I couldn't believe these features. I thought maybe the image was smeared or something."
Hubble next captures the debris being swept back into a comet-like tail by the pressure of sunlight on the tiny dust particles. This stretches out into a debris train where the lightest particles travel the fastest and farthest from the asteroid. The mystery is compounded later when Hubble records the tail splitting in two for a few days.
A multitude of other telescopes on Earth and in space, including NASA's James Webb Space Telescope and Lucy spacecraft, also observed the DART impact and its outcomes.
This Hubble movie is part of a suite of new studies published in the journal Nature about the DART mission. See NASA’s DART Data Validates Kinetic Impact as Planetary Defense Method to learn more.
The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and ESA. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, Maryland, conducts Hubble and Webb science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, in Washington, D.C.
Media Contacts:
Claire Andreoli
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov
Ray Villard
Space Telescope Science Institute, Baltimore, MD
Science Contact:
Jian-Yang Li
Planetary Science Institute, Tucson, AZ







