An international team of researchers has successfully used NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope to map the weather on the hot gas-giant exoplanet WASP-43 b.
Precise brightness measurements over a broad spectrum of mid-infrared light, combined with 3D climate models and previous observations from other telescopes, suggest the presence of thick, high clouds covering the nightside, clear skies on the dayside, and equatorial winds upwards of 5,000 miles per hour mixing atmospheric gases around the planet.
The investigation is just the latest demonstration of the exoplanet science now possible with Webb’s extraordinary ability to measure temperature variations and detect atmospheric gases trillions of miles away.
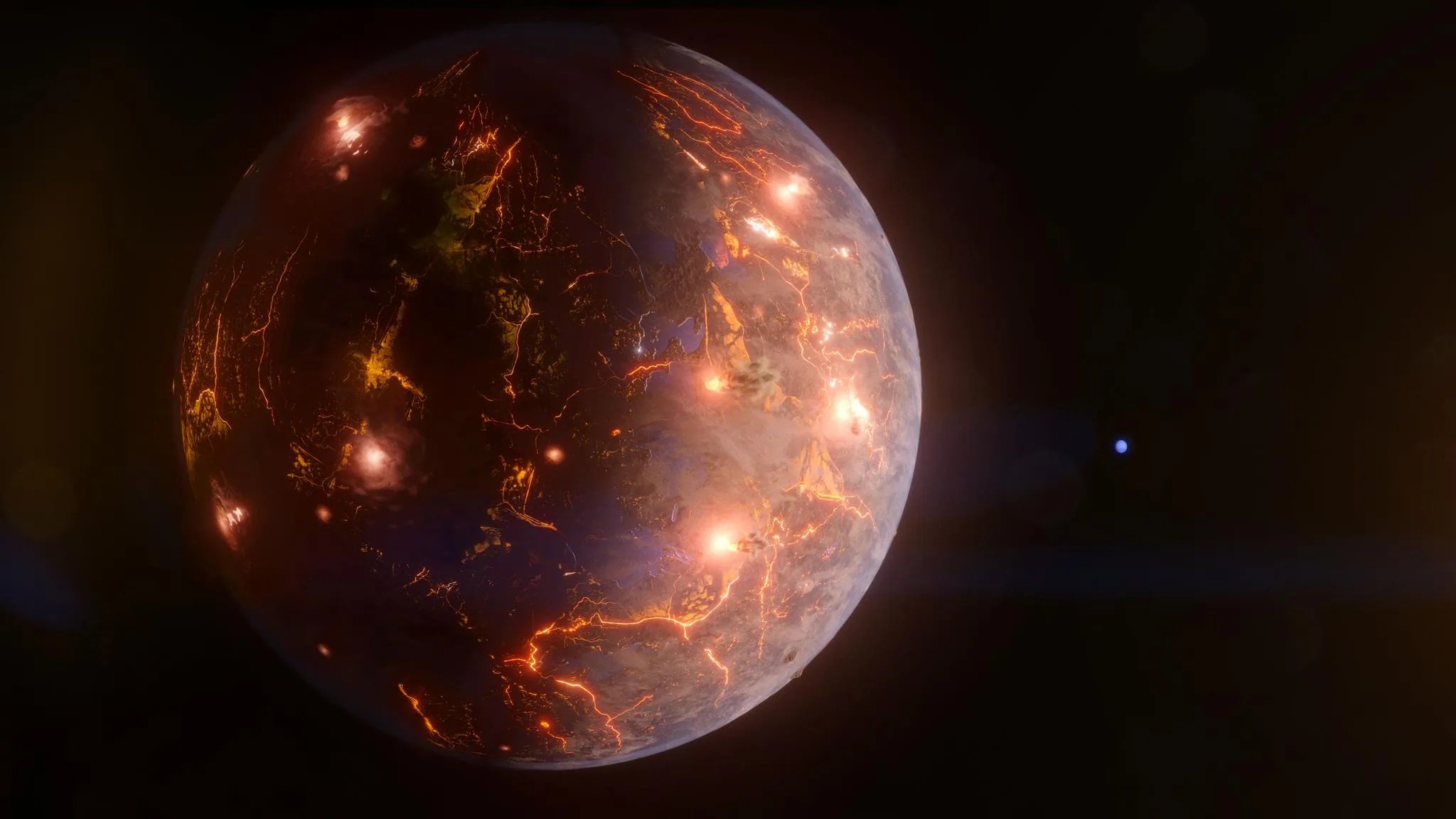
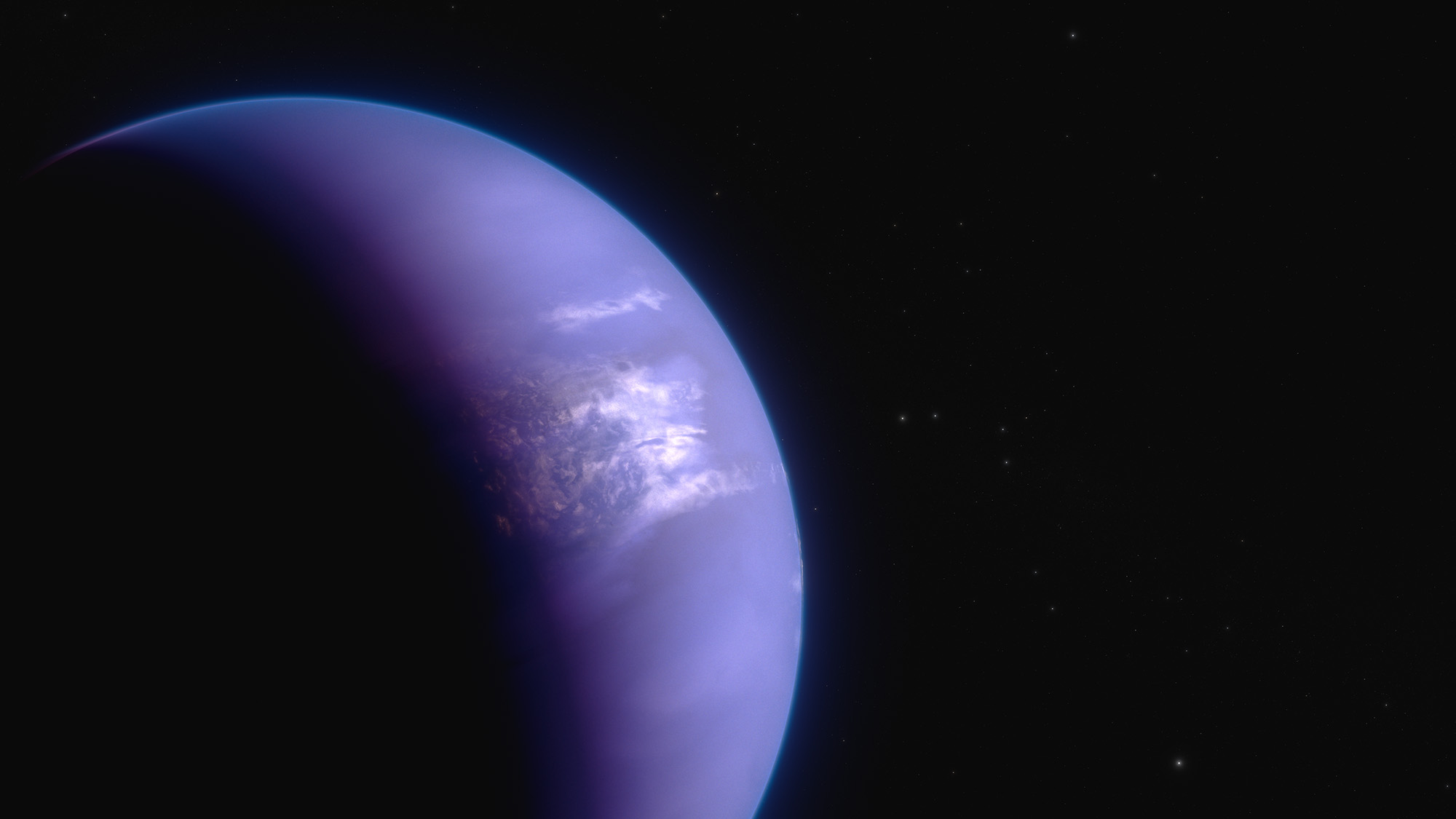
Image: Hot Gas-Giant Exoplanet WASP-43 b (Artist’s Concept)
Tidally Locked “Hot Jupiter”
WASP-43 b is a “hot Jupiter” type of exoplanet: similar in size to Jupiter, made primarily of hydrogen and helium, and much hotter than any of the giant planets in our own solar system. Although its star is smaller and cooler than the Sun, WASP-43 b orbits at a distance of just 1.3 million miles – less than 1/25th the distance between Mercury and the Sun.
With such a tight orbit, the planet is tidally locked, with one side continuously illuminated and the other in permanent darkness. Although the nightside never receives any direct radiation from the star, strong eastward winds transport heat around from the dayside.
Since its discovery in 2011, WASP-43 b has been observed with numerous telescopes, including NASA’s Hubble and now-retired Spitzer space telescopes.
“With Hubble, we could clearly see that there is water vapor on the dayside. Both Hubble and Spitzer suggested there might be clouds on the nightside,” explained Taylor Bell, researcher from the Bay Area Environmental Research Institute and lead author of a study published today in Nature Astronomy. “But we needed more precise measurements from Webb to really begin mapping the temperature, cloud cover, winds, and more detailed atmospheric composition all the way around the planet.”
Mapping Temperature and Inferring Weather
Although WASP-43 b is too small, dim, and close to its star for a telescope to see directly, its short orbital period of just 19.5 hours makes it ideal for phase curve spectroscopy, a technique that involves measuring tiny changes in brightness of the star-planet system as the planet orbits the star.
Since the amount of mid-infrared light given off by an object depends largely on how hot it is, the brightness data captured by Webb can then be used to calculate the planet’s temperature.
Image: Hot Gas-Giant Exoplanet WASP-43 b (MIRI Phase Curve)

The team used Webb’s MIRI (Mid-Infrared Instrument) to measure light from the WASP-43 system every 10 seconds for more than 24 hours. “By observing over an entire orbit, we were able to calculate the temperature of different sides of the planet as they rotate into view,” explained Bell. “From that, we could construct a rough map of temperature across the planet.”
The measurements show that the dayside has an average temperature of nearly 2,300 degrees Fahrenheit (1,250 degrees Celsius) – hot enough to forge iron. Meanwhile, the nightside is significantly cooler at 1,100 degrees Fahrenheit (600 degrees Celsius). The data also helps locate the hottest spot on the planet (the “hotspot”), which is shifted slightly eastward from the point that receives the most stellar radiation, where the star is highest in the planet’s sky. This shift occurs because of supersonic winds, which move heated air eastward.
“The fact that we can map temperature in this way is a real testament to Webb’s sensitivity and stability,” said Michael Roman, a co-author from the University of Leicester in the U.K.
To interpret the map, the team used complex 3D atmospheric models like those used to understand weather and climate on Earth. The analysis shows that the nightside is probably covered in a thick, high layer of clouds that prevent some of the infrared light from escaping to space. As a result, the nightside – while very hot – looks dimmer and cooler than it would if there were no clouds.
Image: Hot Gas-Giant Exoplanet WASP-43 b (Temperature Maps)

Animation: Hot Gas-Giant Exoplanet WASP-43 b (Temperature Maps)
Missing Methane and High Winds
The broad spectrum of mid-infrared light captured by Webb also made it possible to measure the amount of water vapor (H2O) and methane (CH4) around the planet. “Webb has given us an opportunity to figure out exactly which molecules we’re seeing and put some limits on the abundances,” said Joanna Barstow, a co-author from the Open University in the U.K.
The spectra show clear signs of water vapor on the nightside as well as the dayside of the planet, providing additional information about how thick the clouds are and how high they extend in the atmosphere.
Surprisingly, the data also shows a distinct lack of methane anywhere in the atmosphere. Although the dayside is too hot for methane to exist (most of the carbon should be in the form of carbon monoxide), methane should be stable and detectable on the cooler nightside.
“The fact that we don't see methane tells us that WASP-43b must have wind speeds reaching something like 5,000 miles per hour,” explained Barstow. “If winds move gas around from the dayside to the nightside and back again fast enough, there isn’t enough time for the expected chemical reactions to produce detectable amounts of methane on the nightside.”
The team thinks that because of this wind-driven mixing, the atmospheric chemistry is the same all the way around the planet, which wasn’t apparent from past work with Hubble and Spitzer.
The MIRI observation of WASP-43 b was conducted as part of the Webb Early Release Science programs, which are providing researchers with a vast set of robust, open-access data for studying a wide array of cosmic phenomena.The James Webb Space Telescope is the world's premier space science observatory. Webb is solving mysteries in our solar system, looking beyond to distant worlds around other stars, and probing the mysterious structures and origins of our universe and our place in it. Webb is an international program led by NASA with its partners, ESA (European Space Agency) and the Canadian Space Agency.
Downloads
Right click the images in this article to open a larger version in a new tab/window.
Download full resolution images for this article from the Space Telescope Science Institute.
The research results can be viewed in the Nature Astronomy.
Media Contacts
Laura Betz - laura.e.betz@nasa.gov, Rob Gutro - rob.gutro@nasa.gov
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Md.
Margaret Carruthers mcarruthers@stsci.edu, Christine Pulliam - cpulliam@stsci.edu
Space Telescope Science Institute, Baltimore, Md.
More Webb News - https://science.nasa.gov/mission/webb/latestnews/
More Webb Images - https://science.nasa.gov/mission/webb/multimedia/images/
Webb Mission Page - https://science.nasa.gov/mission/webb/
En Español
Para Niños : Qué es una exoplaneta?




