5 min read
New science experiments for NASA are set to launch aboard the agency’s SpaceX 31st commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station. The six investigations aim to contribute to cutting-edge discoveries by NASA scientists and research teams. The SpaceX Dragon spacecraft will liftoff aboard the company’s Falcon 9 rocket from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
Science experiments aboard the spacecraft include a test to study smothering fires in space, evaluating quantum communications, analyzing antibiotic-resistant bacteria, examining health issues like blood clots and inflammation in astronauts, as well as growing romaine lettuce and moss in microgravity.
Developing Firefighting Techniques in Microgravity
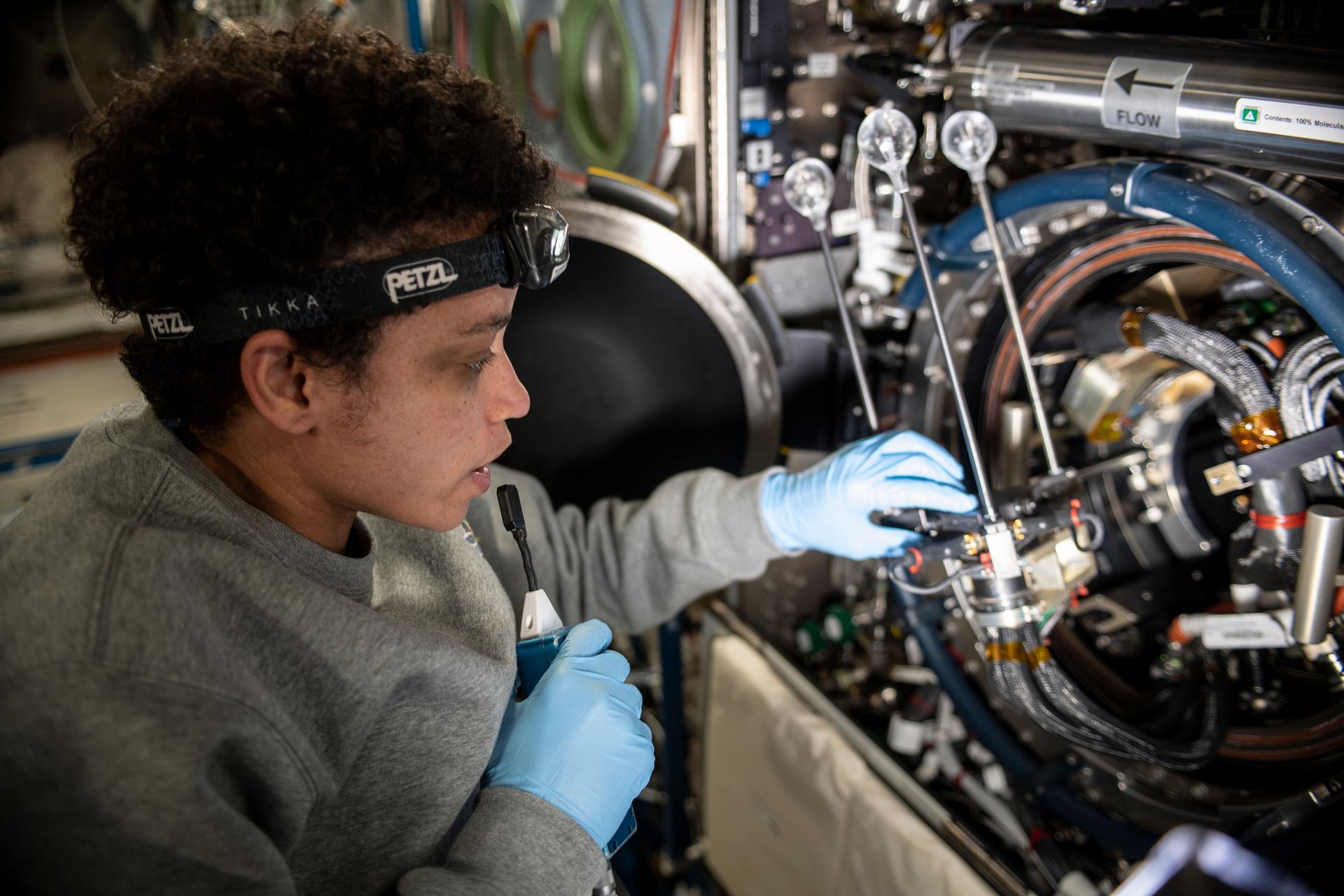
Putting out a fire in space requires a unique approach to prioritize the safety of the spacecraft environment and crew. The SoFIE-MIST (Solid Fuel Ignition and Extinction - Material Ignition and Suppression Test) is one of five investigations chosen by NASA since 2009 to develop techniques on how to contain and put out fires in microgravity. Research from the experiment could strengthen our understanding of the beginning stages of fire growth and behavior, which will assist in building and developing more resilient space establishments and creating better plans for fire suppression in space

Combating Antibiotic Resistance
Resistance to antibiotics is as much of a concern for astronauts in space as it is for humans on Earth. Research determined that the impacts of microgravity can weaken a human’s immune system during spaceflight, which can lead to an increase of infection and illness for those living on the space station.
The GEARS (Genomic Enumeration of Antibiotic Resistance in Space) investigation scans the orbiting outpost for bacteria resistant to antibiotics and these organisms are studied to learn how they thrive and adapt to microgravity. Research results could help increase the safety of astronauts on future missions as well as provide clues to improving human health on Earth.
Understanding Inflammation and Blood Clotting
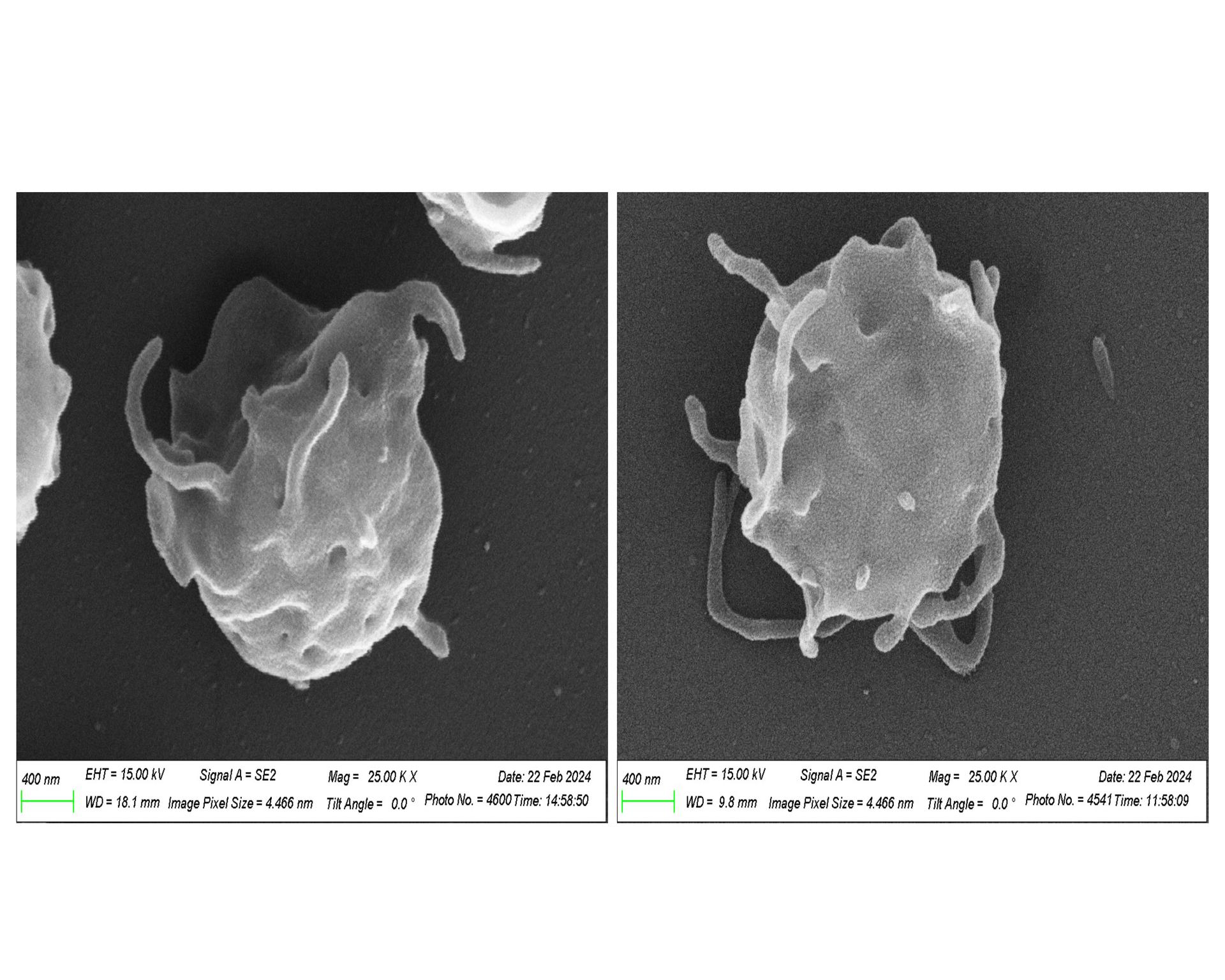
Microgravity takes a toll on the human body and studies have shown that astronauts have had cases of inflammation and abnormally regulated blood clotting. The MeF-1 (Megakaryocytes Orbiting in Outer Space and Near Earth: The MOON Study (Megakaryocyte Flying-One)) investigation will conduct research on how the conditions in microgravity can impact the creation and function of platelets and bone-marrow megakaryocytes. Megakaryocytes, and their progeny, platelets, are key effector cells bridging the inflammatory, immune, and hemostatic continuum.
This experiment could help scientists learn about the concerns caused by any changes in the formation of clots, inflammation, and immune responses both on Earth and during spaceflight.
Building the Space Salad Bar
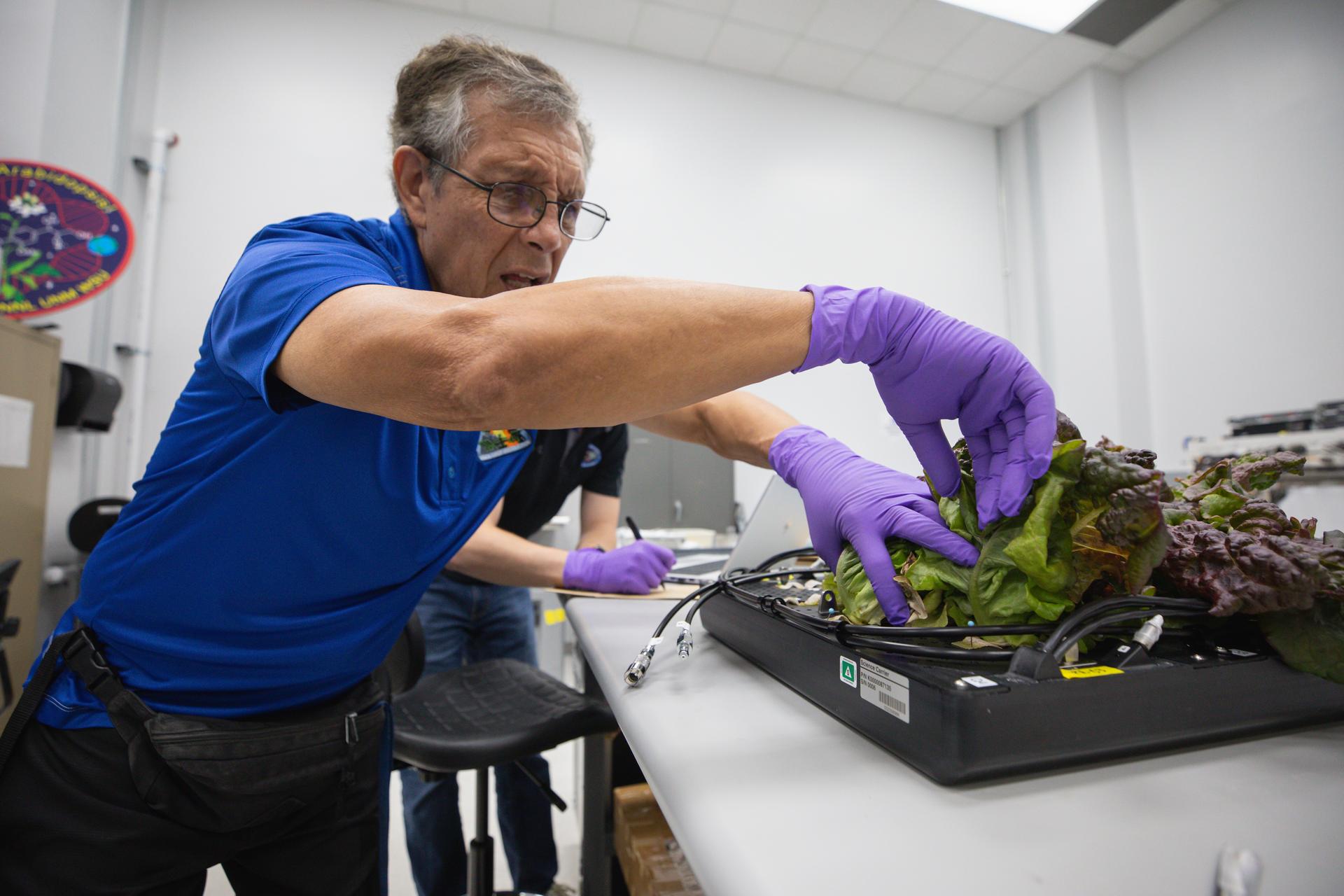
The work continues to grow food in the harsh environment of space that is both nutritious and safe for humans to consume. With Plant Habitat-07, research continues on ‘Outredgeous’ romaine lettuce, first grown on the International Space Station in 2014.
This experiment will sprout this red lettuce in microgravity in the space station’s Advanced Plant Habitat and study how optimal and suboptimal moisture conditions impact plant growth, nutrient content, and the plant microbiome. The knowledge gained will add to NASA’s history of growing vegetables in space and could also benefit agriculture on Earth.

Mixing Moss with Space Radiation
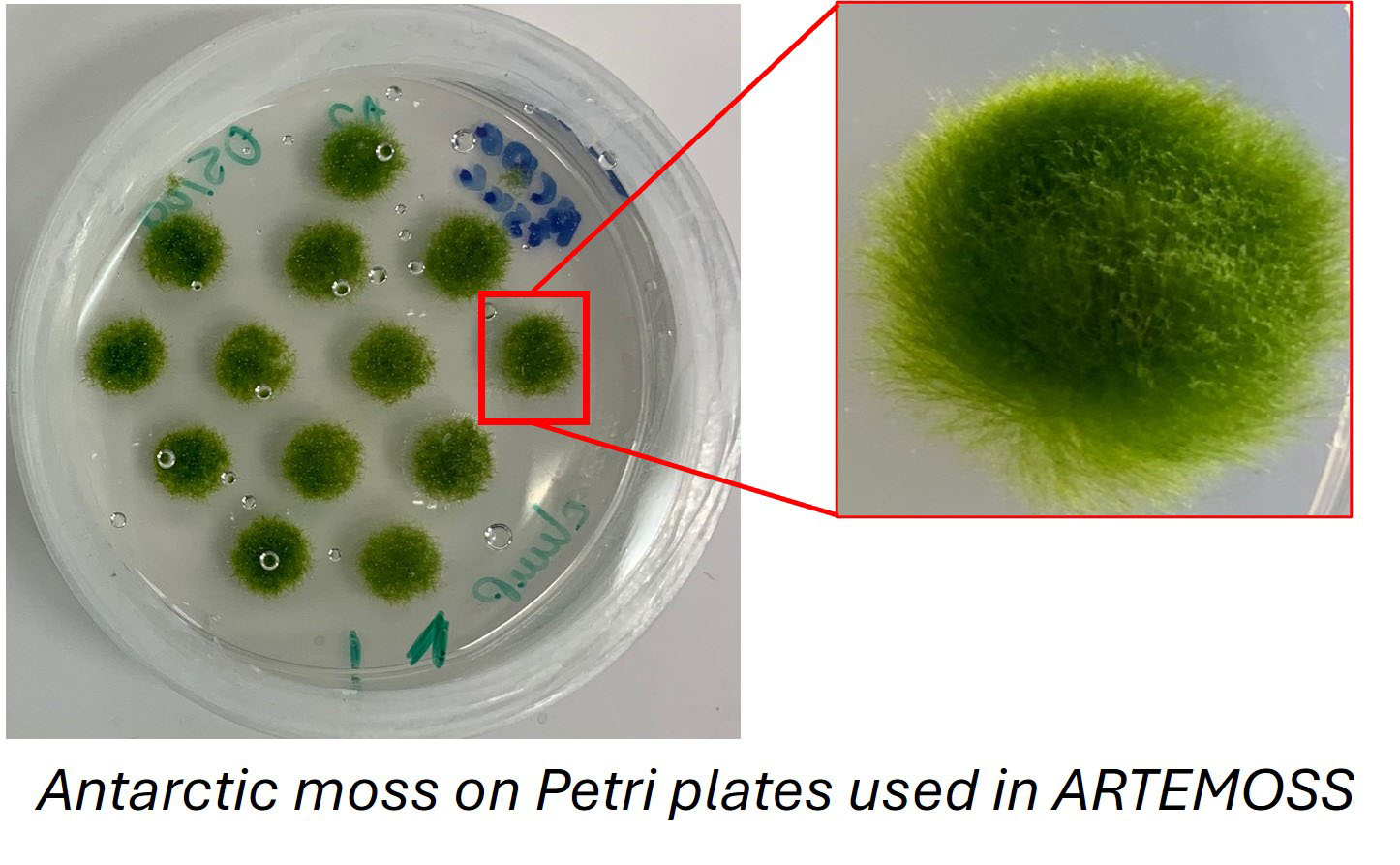
ARTEMOSS (ANT1 Radiation Tolerance Experiment with Moss in Orbit on the Space Station) continues research that started on Earth with samples of Antarctic moss that underwent simulated solar radiation at the NASA Space Radiation Lab at Brookhaven National Lab in Upton, New York.
After exposure to radiation some of the moss samples will spend time on the orbiting outpost in the microgravity environment and some will remain on the ground in the 1g environment. ARTEMOSS will study how Antarctic moss recovers from any potential damage from ionizing radiation exposure when plants remain on the ground and when plants grow in spaceflight microgravity. This study leads the way in understanding the effects of combined simulated cosmic ionizing radiation and spaceflight microgravity on live plants, providing more clues to plant performance in exploration missions to come.

Enabling Communication in Space Between Quantum Computers
The SEAQUE (Space Entanglement and Annealing Quantum Experiment) will experiment with technologies that, if successful, will enable communication on a quantum level using entanglement. Researchers will focus on validating in space a new technology, enabling easier and more robust communication between two quantum systems across large distances. The research from this experiment could lead to developing building blocks for communicating between equipment such as quantum computers with enhanced security.

Related resources:
NASA’s Biological and Physical Sciences Division pioneers scientific discovery and enables exploration by using space environments to conduct investigations not possible on Earth. Studying biological and physical phenomenon under extreme conditions allows researchers to advance the fundamental scientific knowledge required to go farther and stay longer in space, while also benefitting life on Earth.



