1 min read
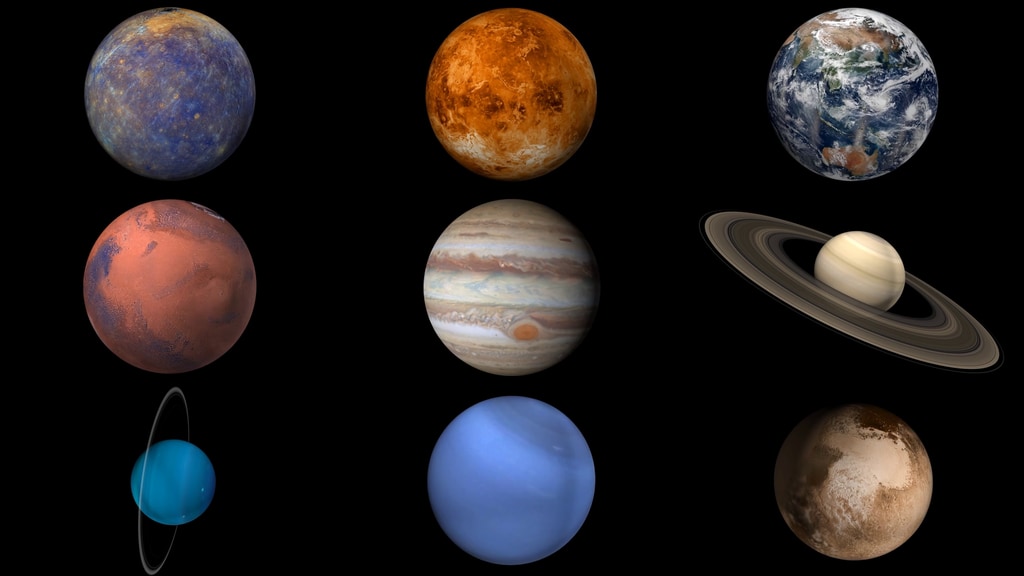

Our solar system has eight planets, and five officially recognized dwarf planets. Which planet is biggest? Which is smallest? What is the order of the planets as we move out from the Sun?
This is a simple guide to the sizes of planets based on the equatorial diameter – or width – at the equator of each planet. Each planet’s width is compared to Earth’s equatorial diameter, which is about 7,926 miles (12,756 kilometers).
At the bottom of the page, there is a handy list of the order of the planets moving away from our Sun.
Sizes of Planets
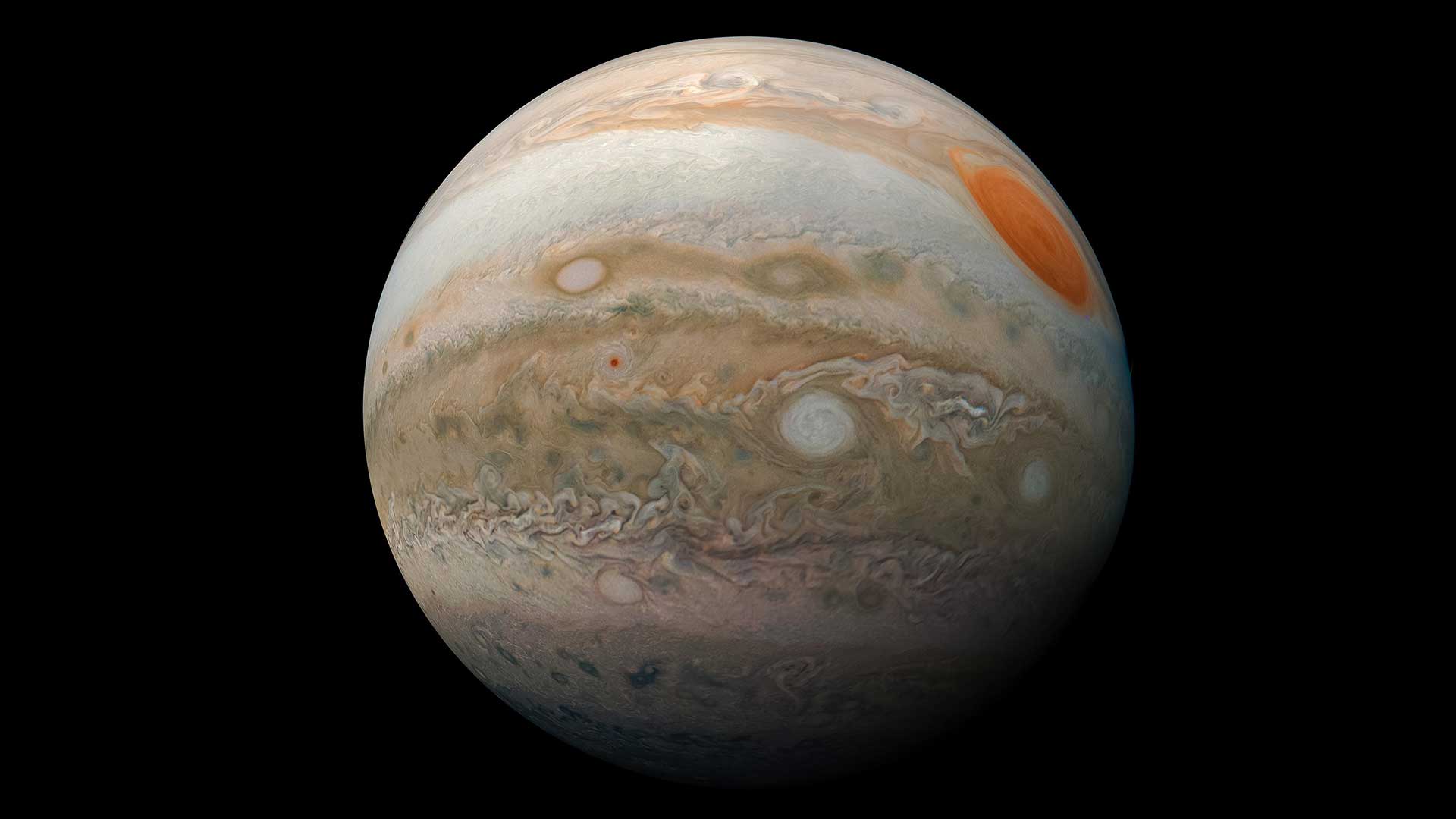 NASA’s Juno spacecraft took three images of Jupiter’s Great Red on Feb. 12, 2019, that were used to create this color-enhanced view. At the time the images were taken, the spacecraft was between 16,700 miles (26,900 kilometers) and 59,300 miles (95,400 kilometers) above Jupiter's cloud tops.Enhanced image by Kevin M. Gill (CC-BY) based on images provided courtesy of NASA/JPL-Caltech/SwRI/MSSS01
NASA’s Juno spacecraft took three images of Jupiter’s Great Red on Feb. 12, 2019, that were used to create this color-enhanced view. At the time the images were taken, the spacecraft was between 16,700 miles (26,900 kilometers) and 59,300 miles (95,400 kilometers) above Jupiter's cloud tops.Enhanced image by Kevin M. Gill (CC-BY) based on images provided courtesy of NASA/JPL-Caltech/SwRI/MSSS01Jupiter
Jupiter is the largest planet in the solar system. It’s about 11 times wider than Earth with an equatorial diameter of 88,846 miles (about 142,984 kilometers). Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun, orbiting at an average distance of 483.7 million miles (778 million kilometers). It’s about five times farther from the Sun than Earth.
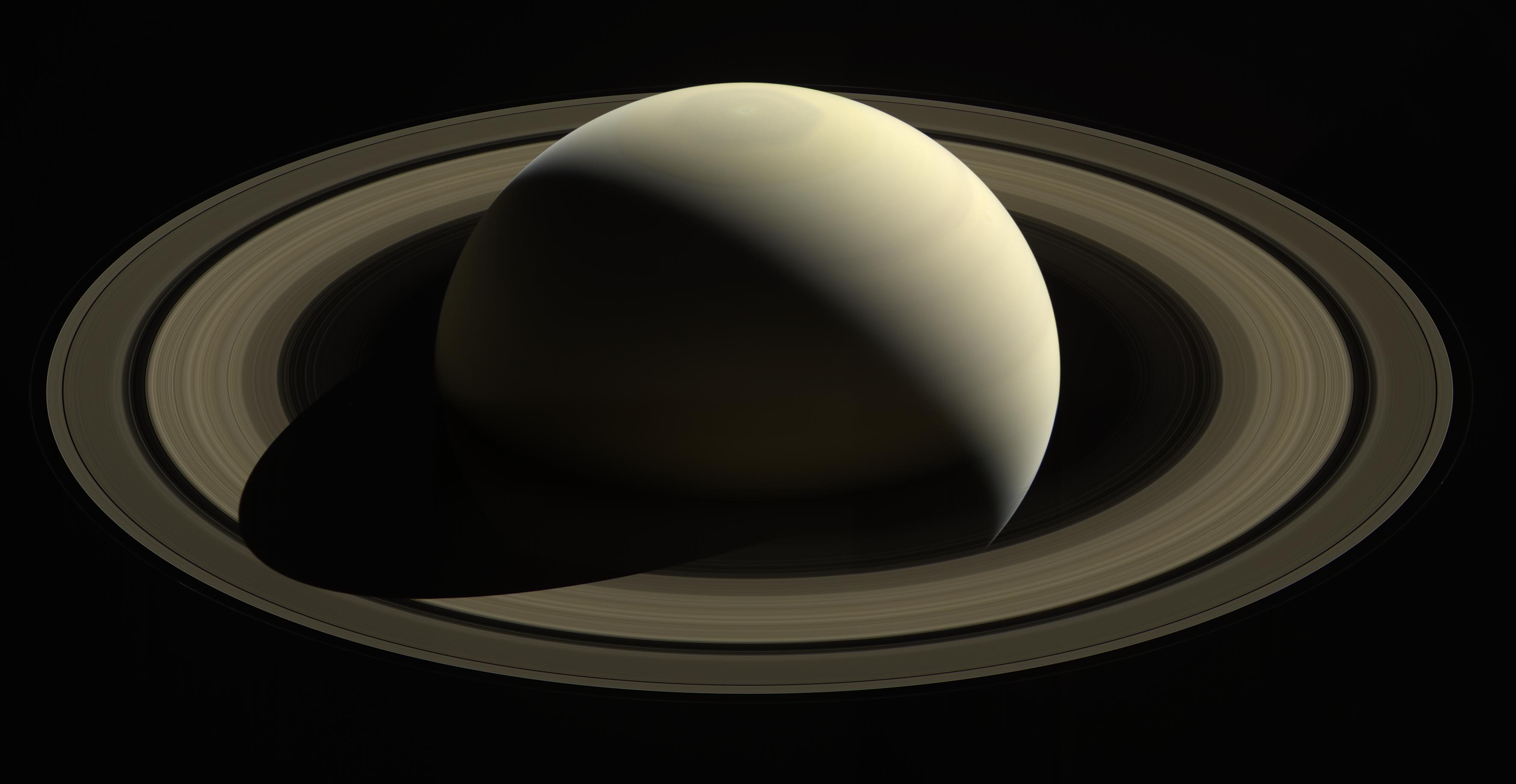 NASA’s Cassini spacecraft captured one of its last looks at Saturn, and its main rings from a distance. The images used to create this view were taken on Oct. 28, 2016. The spacecraft arrived at Saturn in 2004, and the mission ended Sept.15, 2017.02
NASA’s Cassini spacecraft captured one of its last looks at Saturn, and its main rings from a distance. The images used to create this view were taken on Oct. 28, 2016. The spacecraft arrived at Saturn in 2004, and the mission ended Sept.15, 2017.02Saturn
Saturn, known for its spectacular icy rings, is the second largest planet in our solar system. It’s about nine times wider than Earth, with an equatorial diameter of about 74,898 miles (about 120,536 kilometers). Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun, orbiting at an average distance of 889.8 million miles (1.4 billion kilometers). It’s about 9.5 times farther from the Sun than Earth.
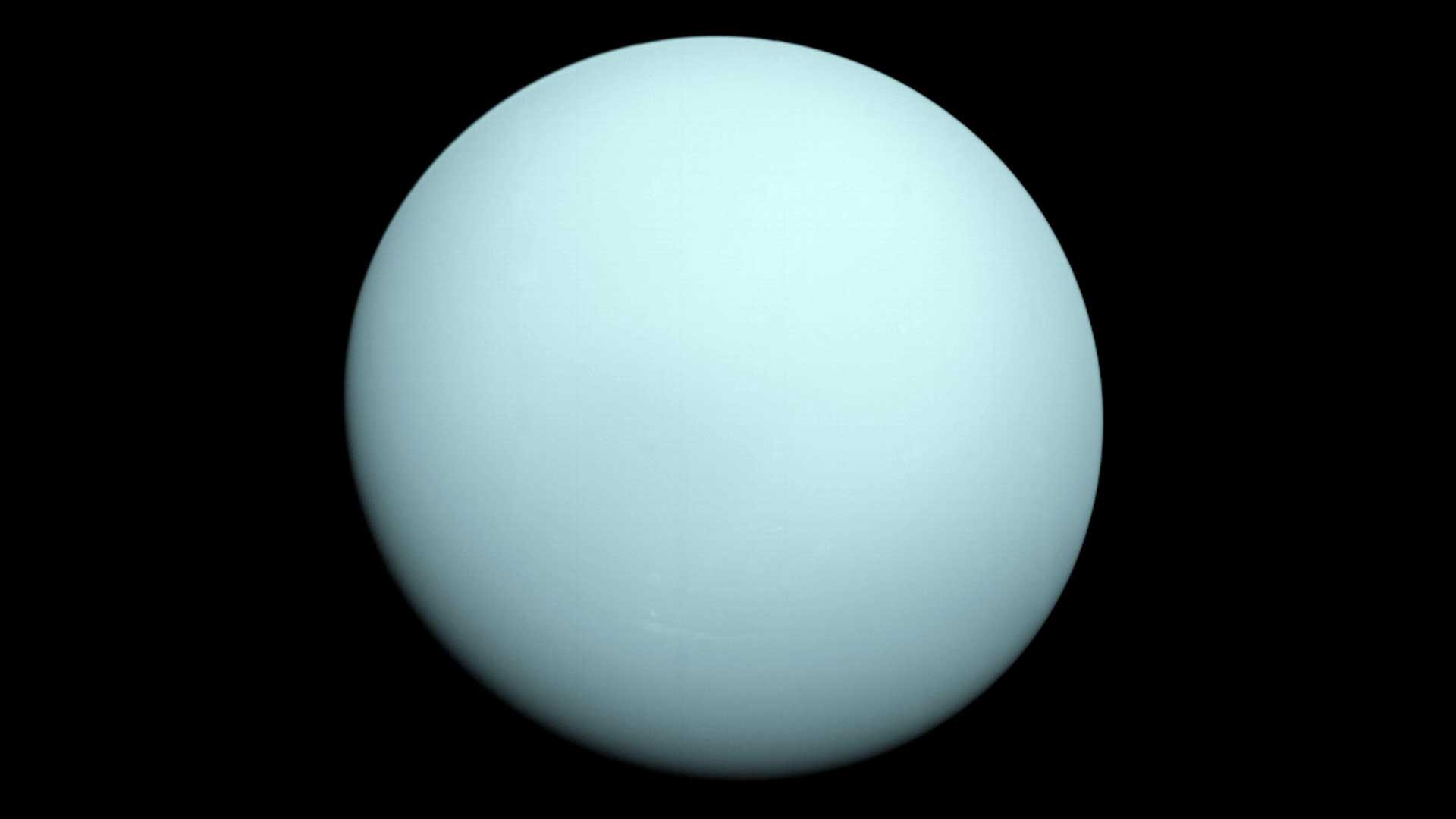 An image of the planet Uranus taken by the spacecraft Voyager 2 in 1986.NASA/JPL-Caltech03
An image of the planet Uranus taken by the spacecraft Voyager 2 in 1986.NASA/JPL-Caltech03Uranus
Uranus is the third largest planet in our solar system. It’s about four times wider than Earth, and has an equatorial diameter of about 31,763 miles (51,118 kilometers). Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun, orbiting at an average distance of 1.8 billion miles (2.9 billion kilometers). It’s about 19 times farther from the Sun than Earth.
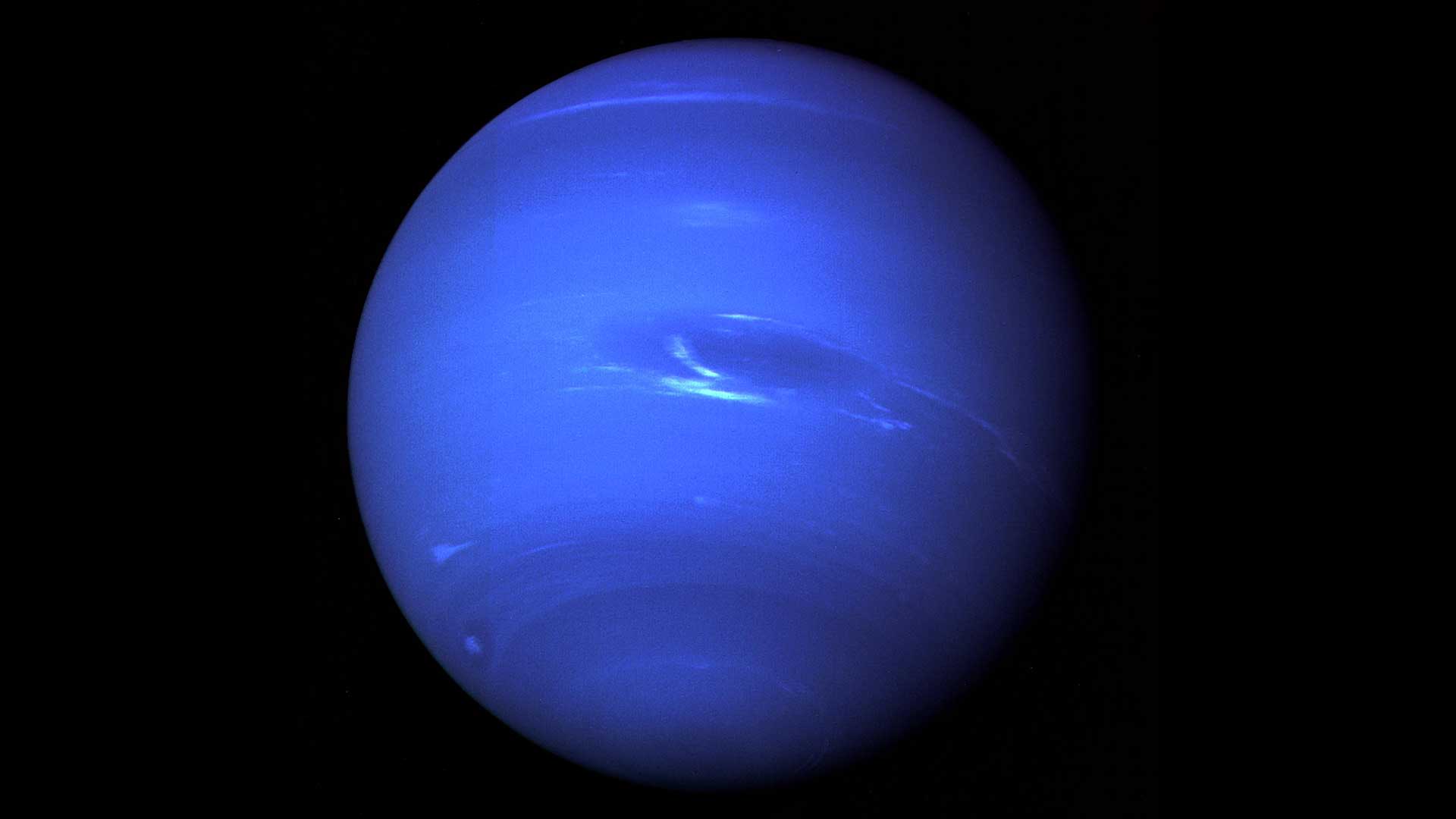 This picture of Neptune was produced from images taken by NASA’s Voyager 2 in the summer of 1989 as it became the first spacecraft to fly by the planet.NASA/JPL-Caltech04
This picture of Neptune was produced from images taken by NASA’s Voyager 2 in the summer of 1989 as it became the first spacecraft to fly by the planet.NASA/JPL-Caltech04Neptune
Neptune is the fourth largest planet. It’s about four times wider than Earth with an equatorial diameter of about 30,775 miles (49,528 kilometers). Neptune is the eighth, and the most distant planet from the Sun, orbiting at an average distance of 2.8 billion miles (4.5 billion kilometers). Neptune is about 30 times farther from the Sun than Earth.
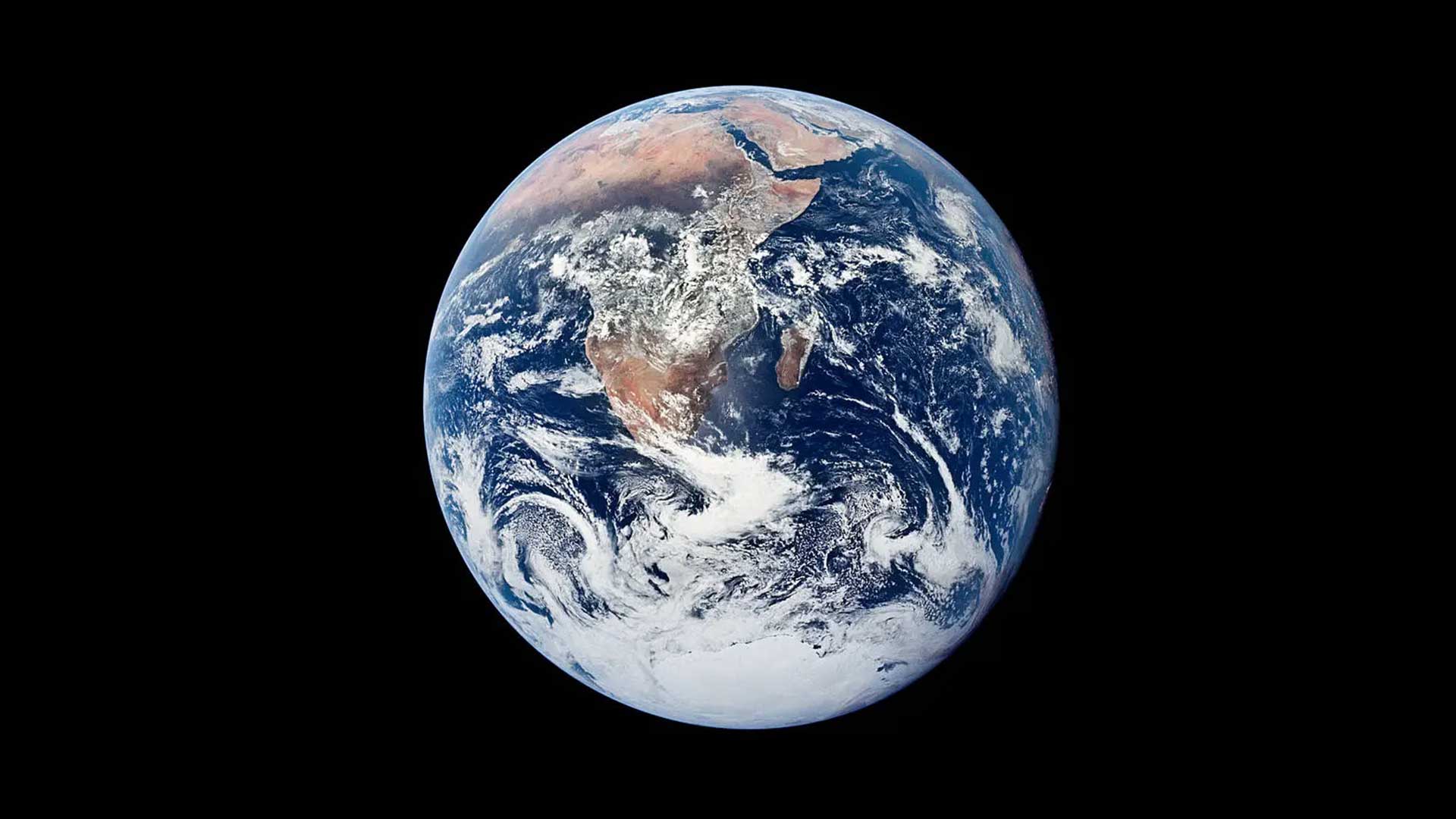 This classic photograph of the Earth was taken on Dec. 7, 1972, by the crew of the final Apollo mission, Apollo 17, as it traveled toward the Moon.NASA05
This classic photograph of the Earth was taken on Dec. 7, 1972, by the crew of the final Apollo mission, Apollo 17, as it traveled toward the Moon.NASA05Earth
Earth is the fifth largest planet in the solar system. It has an equatorial diameter of about 7,926 miles (12,756 kilometers). Earth is the third planet from the Sun, orbiting at an average distance of 93 million miles (149.7 million kilometers).
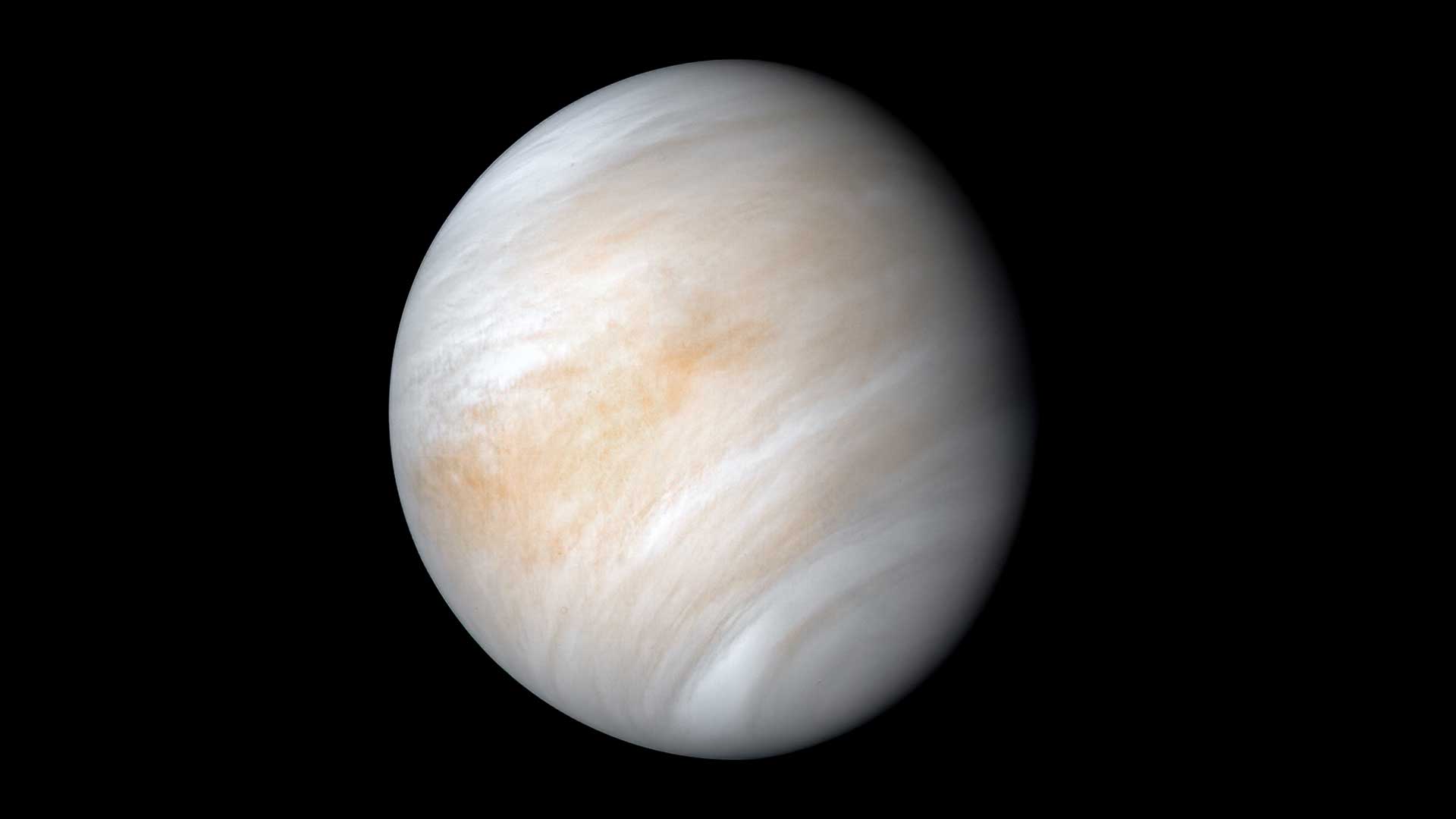 As it sped away from Venus in February 1974, NASA's Mariner 10 spacecraft captured this seemingly peaceful view of Venus. But, contrary to its serene appearance, Venus is a world of intense heat, crushing atmospheric pressure and clouds of corrosive acid.NASA/JPL-Caltech06
As it sped away from Venus in February 1974, NASA's Mariner 10 spacecraft captured this seemingly peaceful view of Venus. But, contrary to its serene appearance, Venus is a world of intense heat, crushing atmospheric pressure and clouds of corrosive acid.NASA/JPL-Caltech06Venus
Venus is the sixth largest planet in the solar system. Venus is about the same width as Earth, and has an equatorial diameter of about 7,521 miles (12,104 kilometers). For this reason, Venus is sometimes known as Earth’s twin. Venus is the second planet from the Sun, orbiting at an average distance of 67.2 million miles (108 million kilometers). Venus is about 26 million miles (42 million kilometers) closer to the Sun than Earth.
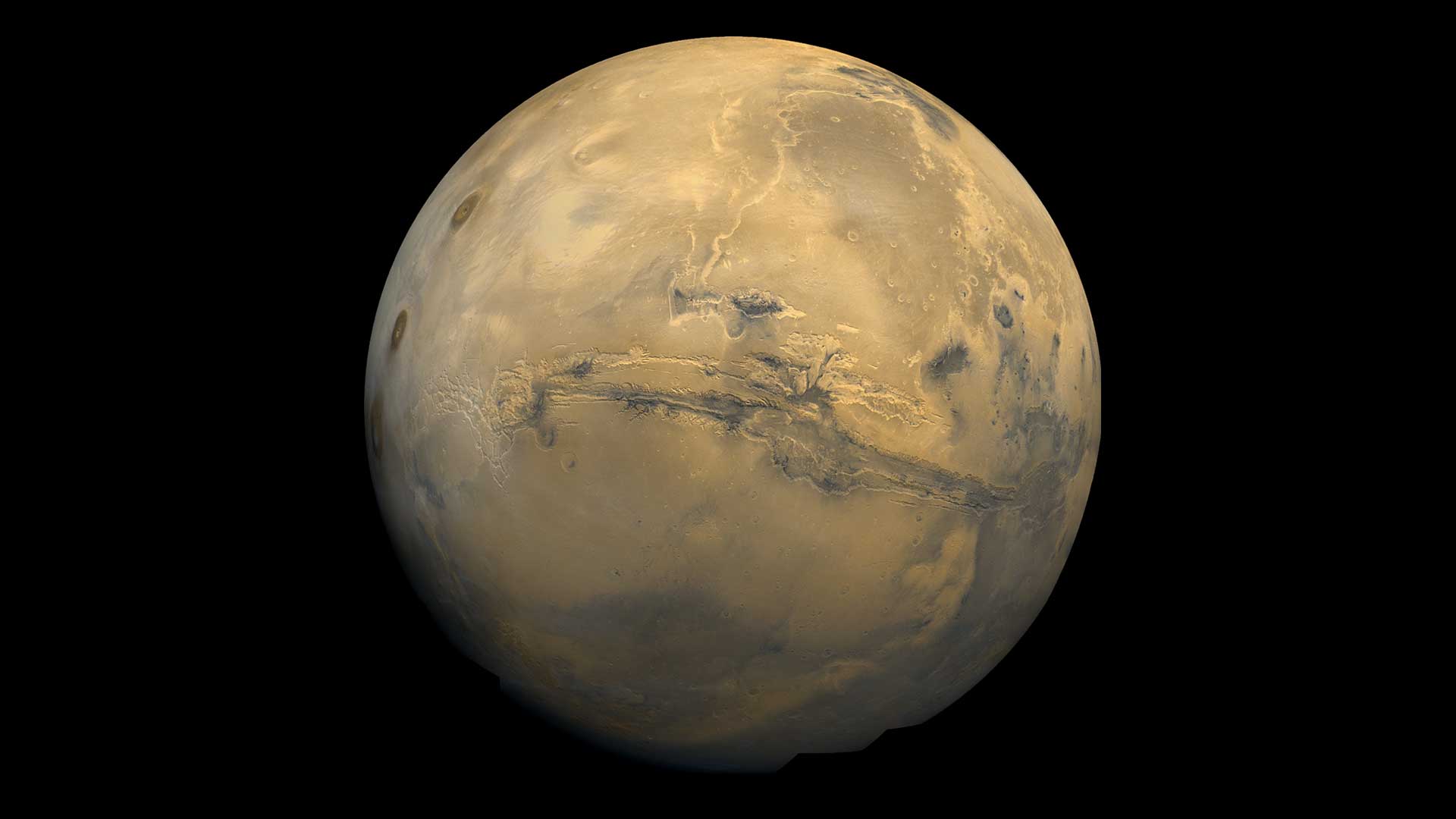 The global mosaic of Mars was created using Viking 1 Orbiter images taken in February 1980. The mosaic shows the entire Valles Marineris canyon system stretching across the center of Mars. It’s more than 2,000 miles (3,000 kilometers) long, 370 miles (600 kilometers) wide and 5 miles (8 kilometers) deep.NASA07
The global mosaic of Mars was created using Viking 1 Orbiter images taken in February 1980. The mosaic shows the entire Valles Marineris canyon system stretching across the center of Mars. It’s more than 2,000 miles (3,000 kilometers) long, 370 miles (600 kilometers) wide and 5 miles (8 kilometers) deep.NASA07Mars
Mars, the red planet, is the seventh largest planet in our solar system. Mars is about half the width of Earth, and has an equatorial diameter of about 4,221 miles (6,792 kilometers). Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun, orbiting at an average distance of 141.6 million miles (227.9 million kilometers). Mars is about 49 million miles (79 million kilometers) farther from the Sun than Earth.
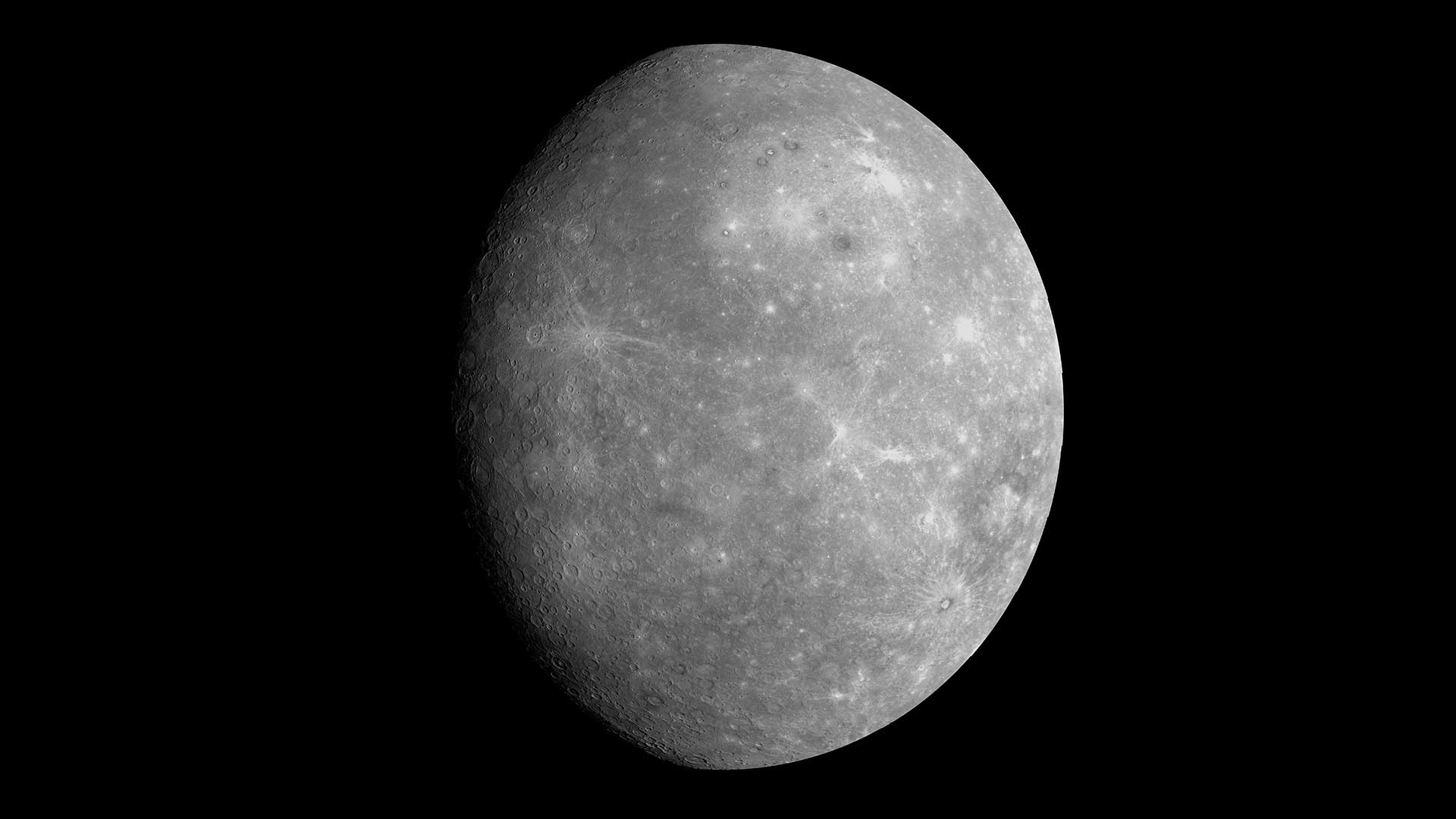 Mercury's Caloris basin is prominently featured in this view from NASA's MESSENGER spacecraft. Just south of Caloris lies the Mozart basin. Toward the center of the globe, Tolstoj is visible. Beethoven basin is just visible along the eastern edge of the globe.NASA/Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory/Carnegie Institution of Washington08
Mercury's Caloris basin is prominently featured in this view from NASA's MESSENGER spacecraft. Just south of Caloris lies the Mozart basin. Toward the center of the globe, Tolstoj is visible. Beethoven basin is just visible along the eastern edge of the globe.NASA/Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory/Carnegie Institution of Washington08Mercury
Mercury is the smallest planet in our solar system. Mercury is a little more than one-third the width of Earth, and has an equatorial diameter of about 3,032 miles (4,880 kilometers). Mercury is the closest planet to the Sun, orbiting at an average distance of 36 million miles (58 million kilometers). Mercury is 57 million miles closer to the Sun than Earth.
Sizes of Dwarf Planets
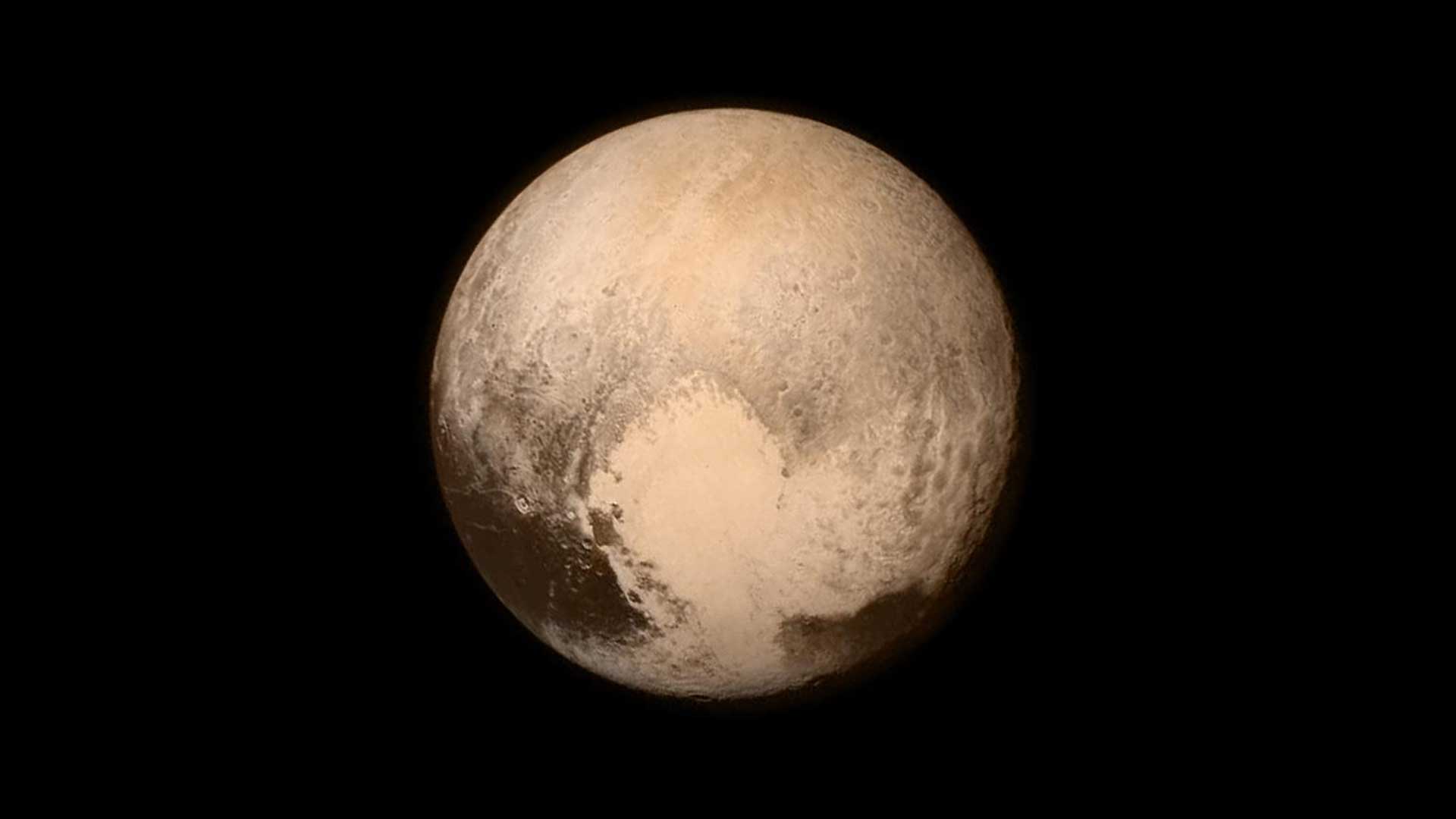 Pluto nearly fills the frame in this image from NASA’s New Horizons spacecraft taken on July 13, 2015, when the spacecraft was 476,000 miles (768,000 kilometers) from the surface. This is the last and most detailed image sent to Earth before the spacecraft's closest approach to Pluto on July 14, 2015.NASA/JHUAPL/SwRI01
Pluto nearly fills the frame in this image from NASA’s New Horizons spacecraft taken on July 13, 2015, when the spacecraft was 476,000 miles (768,000 kilometers) from the surface. This is the last and most detailed image sent to Earth before the spacecraft's closest approach to Pluto on July 14, 2015.NASA/JHUAPL/SwRI01Pluto
Pluto is the largest dwarf planet in our solar system, just slightly larger than Eris, at number two. Pluto has an equatorial diameter of about 1,477 miles (2,377 kilometers). Pluto is about 1/5th the width of Earth. Pluto orbits the Sun at a distance of about 3.67 billion miles (5.9 billion kilometers), or about 39 times farther away than Earth from the Sun.
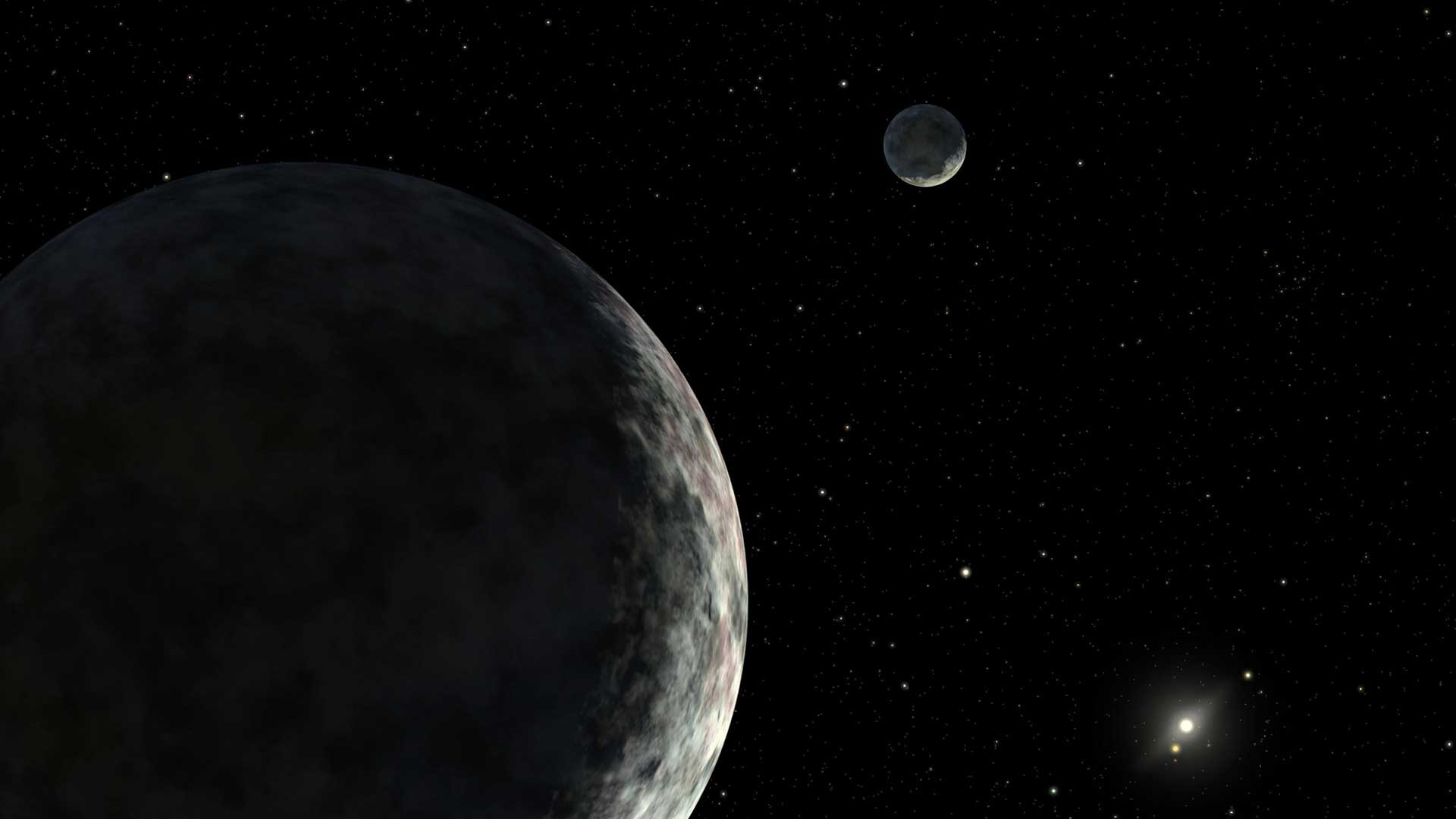 An artist's concept of dwarf planet Eris and its moon Dysnomia. The Sun is the small star in the distance.NASA/JPL-Caltech02
An artist's concept of dwarf planet Eris and its moon Dysnomia. The Sun is the small star in the distance.NASA/JPL-Caltech02Eris
Eris is the second largest dwarf planet with an equatorial diameter of about 1,445 miles (about 2,326 kilometers). Eris is about 1/5th the width of Earth. It orbits the Sun from an average distance of 6.3 billion miles (10 billion kilometers). Eris is about 68 times farther from the Sun than Earth.
 This Hubble image shows dwarf planet Haumea in the center, and its two moons – Namaka and Hi'iak. The image was processed with data gathered by Hubble’s Wide Field Camera 3 using the Ultraviolet-Visible channel on June 30, 2015.NASA, ESA, and D. Ragozzine (Brigham Young University); Image Processing: Gladys Kober (NASA/Catholic University of America)03
This Hubble image shows dwarf planet Haumea in the center, and its two moons – Namaka and Hi'iak. The image was processed with data gathered by Hubble’s Wide Field Camera 3 using the Ultraviolet-Visible channel on June 30, 2015.NASA, ESA, and D. Ragozzine (Brigham Young University); Image Processing: Gladys Kober (NASA/Catholic University of America)03Haumea
Haumea is the third largest dwarf planet with an equatorial diameter of about 1,080 miles (about 1,740 kilometers). Haumea is about 1/7 the width of Earth. It orbits the Sun from an average distance of 4 billion miles (6.5 billion kilometers), and it’s about 43 times farther from the Sun than Earth.
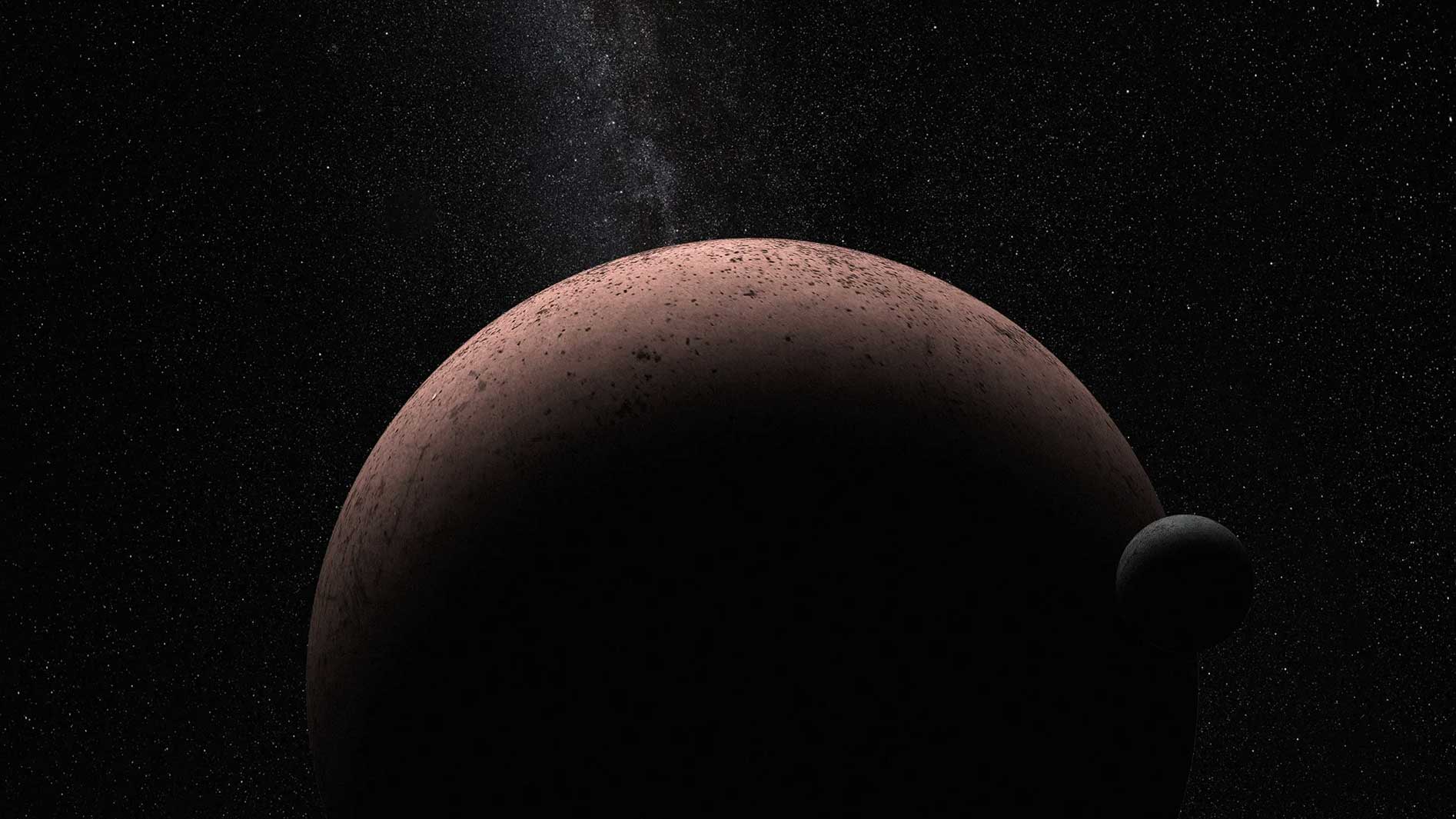 This artist's illustration shows dwarf planet Makemake and its moon, nicknamed MK 2.NASA04
This artist's illustration shows dwarf planet Makemake and its moon, nicknamed MK 2.NASA04Makemake
The fourth largest dwarf planet in the solar system, Makemake has an equatorial diameter of about 891 miles (about 1,434 kilometers). Makemake is 1/9 the width of Earth. Makemake orbits the Sun from an average distance of 4.3 billion miles (6.9 billion kilometers), and it’s about 46 times farther from the Sun than is Earth.
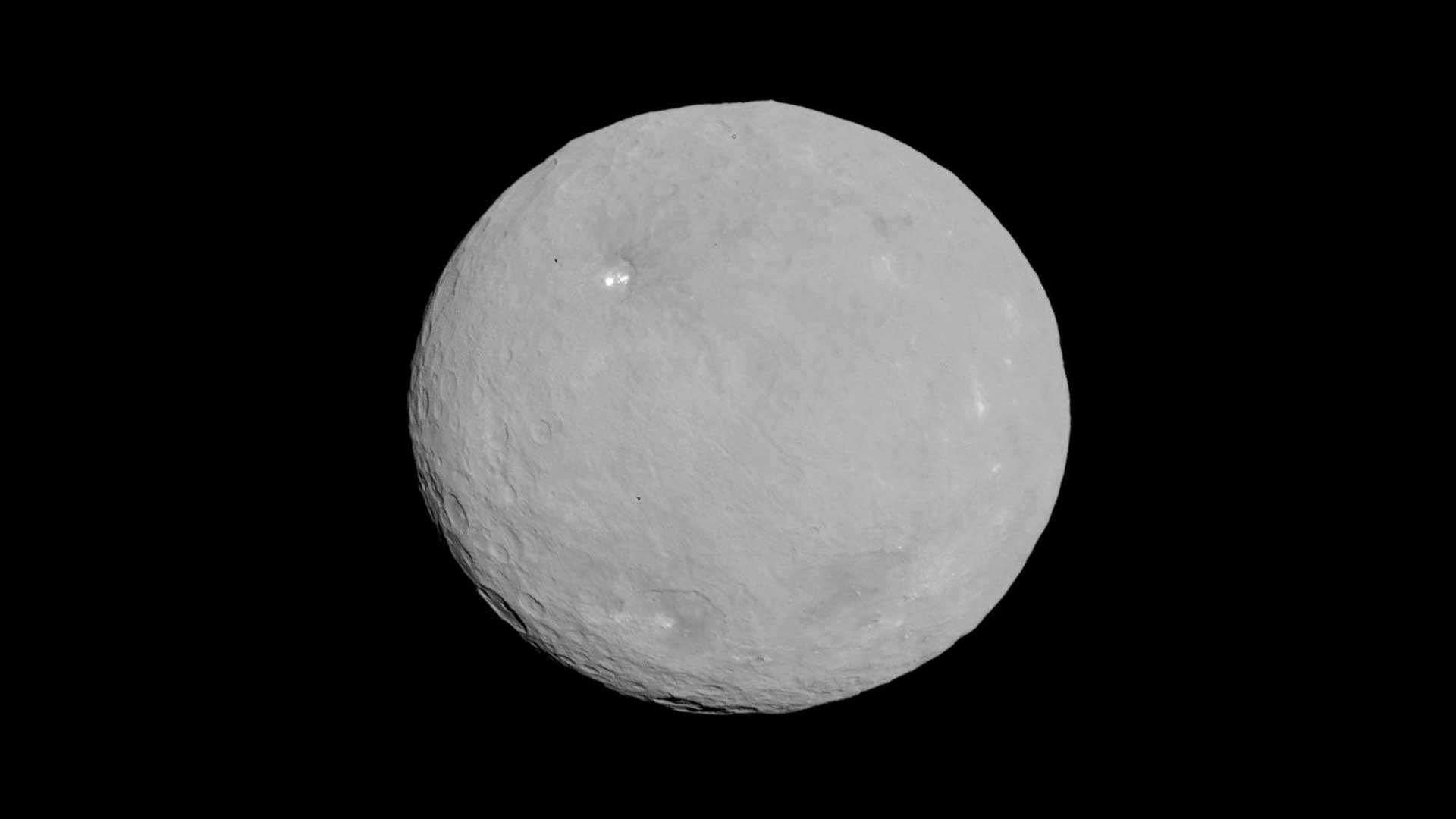 This image of Ceres is part of a sequence taken by NASA's Dawn spacecraft on May 5 and 6, 2015, from a distance of 8,400 miles (13,600 kilometers).NASA/JPL-Caltech/UCLA/MPS/DLR/IDA05
This image of Ceres is part of a sequence taken by NASA's Dawn spacecraft on May 5 and 6, 2015, from a distance of 8,400 miles (13,600 kilometers).NASA/JPL-Caltech/UCLA/MPS/DLR/IDA05Ceres
Ceres is the smallest dwarf planet with an equatorial diameter of about 599 miles (about 964 kilometers). Ceres is about 1/13 the width of Earth. The closest dwarf planet to the Sun, and the only dwarf planet in the inner solar system, Ceres orbits the Sun from an average distance of 257 million miles (413 million kilometers) Ceres is about 2.8 times farther from the Sun than Earth.
Order of Planets and Dwarf Planets - Distance From the Sun
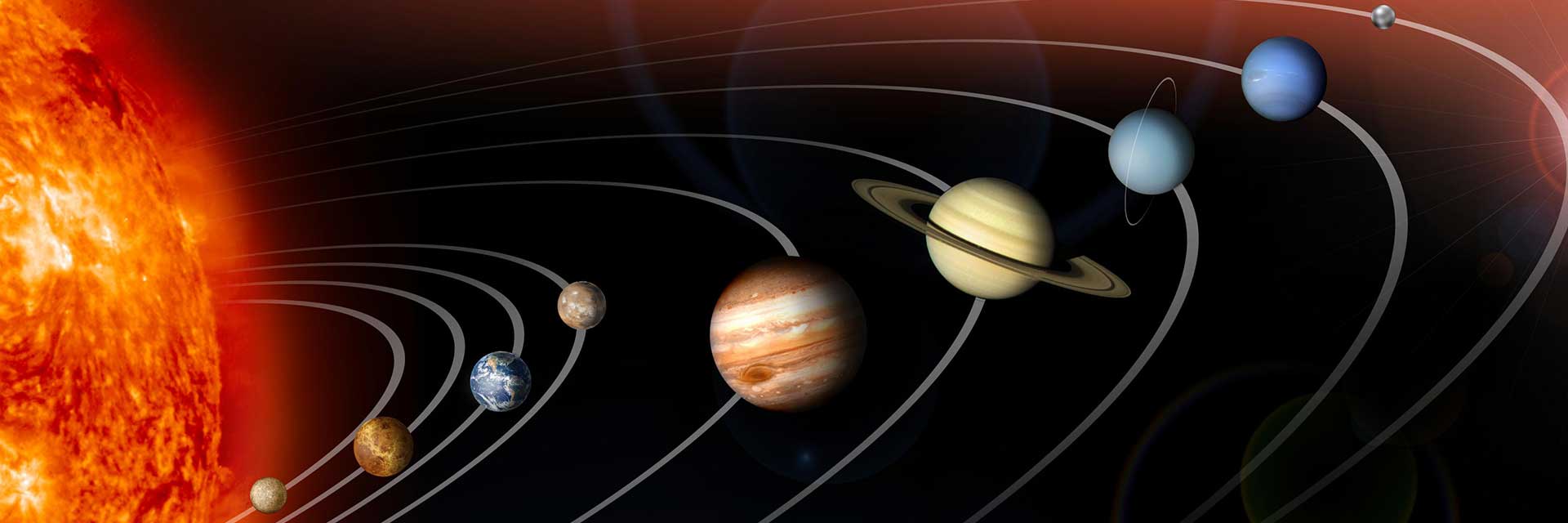
- Mercury: 36 million miles (58 million kilometers)
- Venus: 67.2 million miles (108 million kilometers)
- Earth: 93 million miles (149.7 million kilometers)
- Mars: 141.6 million miles (227.9 million kilometers)
- Dwarf planet Ceres: 257 million miles (413 million kilometers)
- Jupiter: 483.7 million miles (778 million kilometers)
- Saturn: 889.8 million miles (1.4 billion kilometers)
- Uranus: 1.8 billion miles (2.9 billion kilometers)
- Neptune: 2.8 billion miles (4.5 billion kilometers)
- Dwarf Planet Pluto: 3.67 billion miles (5.9 billion kilometers)
- Dwarf Planet Haumea: 4 billion miles (6.5 billion kilometers)
- Dwarf Planet Makemake: 4.3 billion miles (6.9 billion kilometers)
- Dwarf Planet Eris: 6.3 billion miles (10 billion kilometers)



