To fulfill the mission’s top-level science objectives, Roman will conduct three core community surveys plus a suite of general astrophysics surveys using the Wide Field Instrument (WFI), along with a set of technology demonstration observations undertaken with the Coronagraph Instrument. The core surveys include the High-Latitude Wide-Area Survey, Galactic Bulge Time-Domain Survey, and High-Latitude Time-Domain Survey.
Links below describe the core surveys, which are still being defined through an open, community-driven process. The General Astrophysics observing programs, as well as funding to work with Roman data, will be competed and selected through future processes. The surveys and programs all relate to at least two of the mission’s three main science themes: measuring dark energy, investigating exoplanets, and great observatory astrophysics and planetary science.
All Roman observations will be publicly available with no period of limited access.
Core Community Surveys
Galactic Bulge Time-Domain Survey
Tracking how stars change in brightness over time to discover distant worlds
Tracking how hundreds of millions of stars change in brightness will unveil thousands of newfound worlds with a wide range of characteristics (including rogue planets) and isolated stellar-mass black holes.
Read More
High-Latitude Time-Domain Survey
Revealing the dynamic universe beyond our galaxy
Astronomers will use this survey to probe our dynamic universe by observing the same region of the cosmos every five days for two years. Stitching these observations together will create movies that will uncover a wealth of transient objects, like exploding stars, stars being swept into black holes, and neutron star mergers.
Read More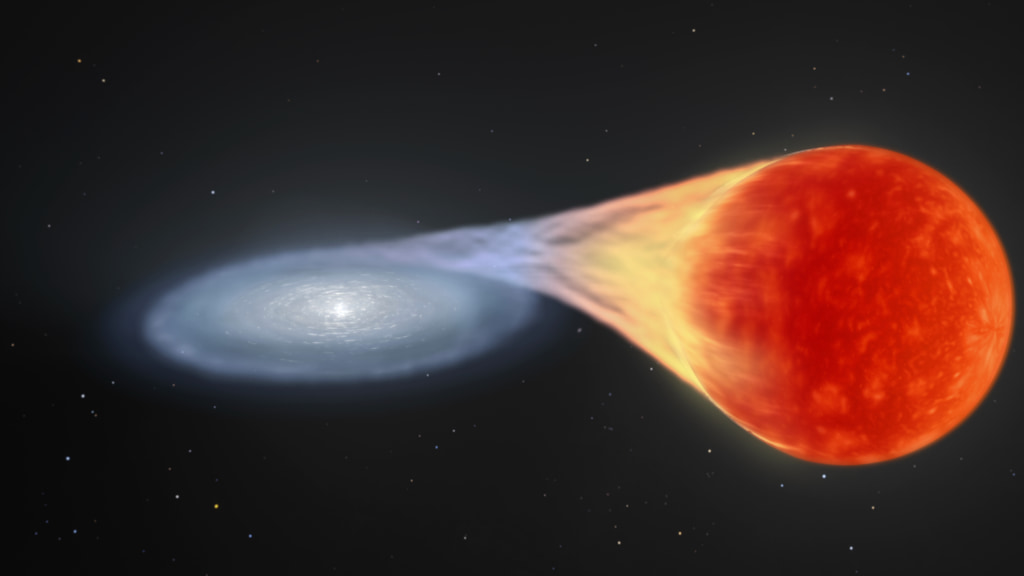
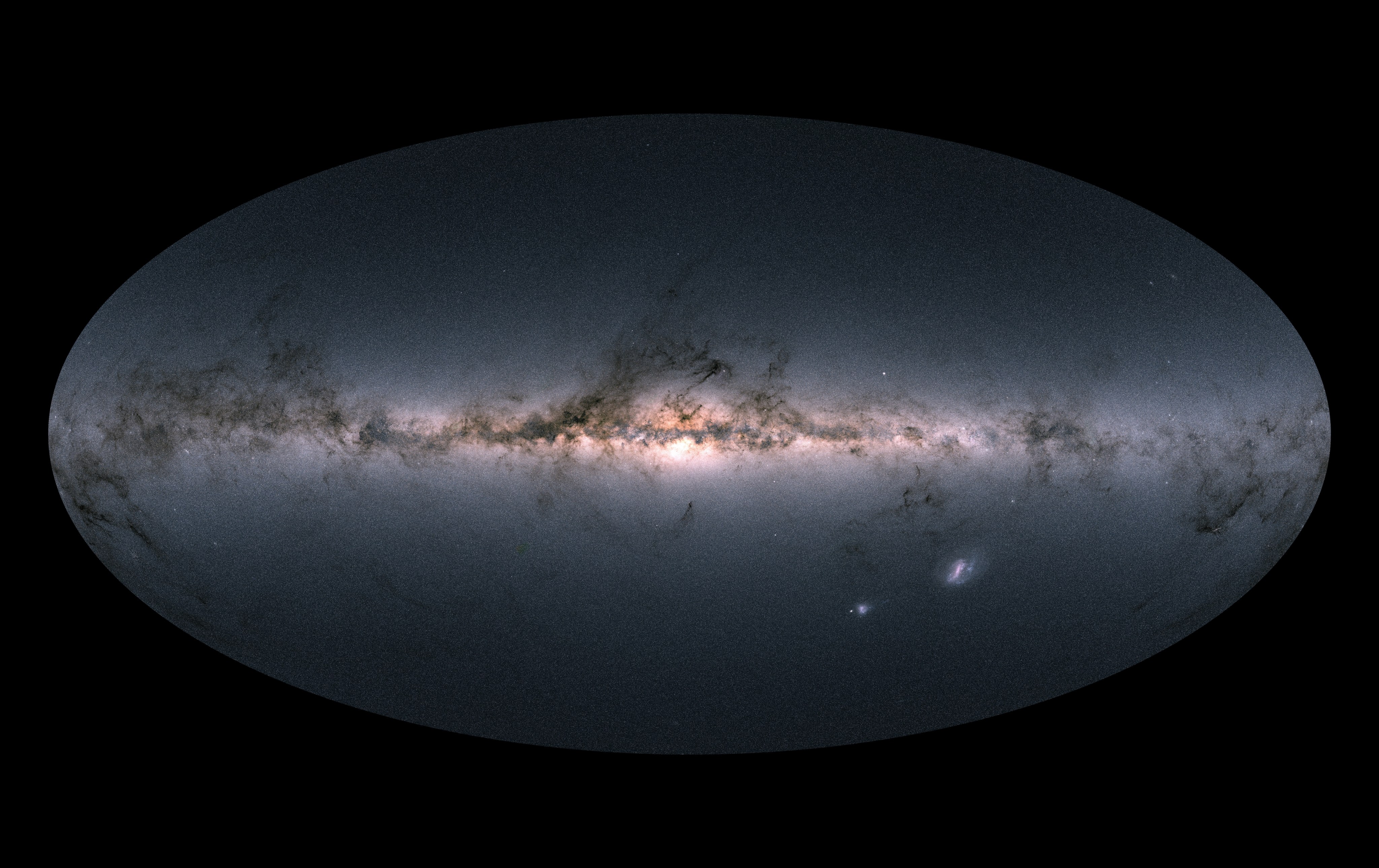
High-Latitude Wide-Area Survey
Making a 3D map of the universe
This survey will combine the powers of imaging and spectroscopy to uncover hundreds of millions of galaxies. Roman's wide and deep 3D images will allow astronomers to explore the structure and expansion of the universe as it evolved through cosmic time.
Read More
Imaging Exoplanets
Roman will demonstrate direct imaging technology by observing worlds that are Jupiter’s size circling Sun-like stars, and photographing planets that are up to several billion years old – something that has never been done before. These results will pave the way for future missions to study worlds that are even more Earth-like.
Learn More
General Astrophysics
Since Roman’s core surveys will enable a wide range of investigations and the mission will conduct additional observations, Roman’s science haul will extend far beyond the primary goals of untangling dark energy and discovering new worlds.
Learn More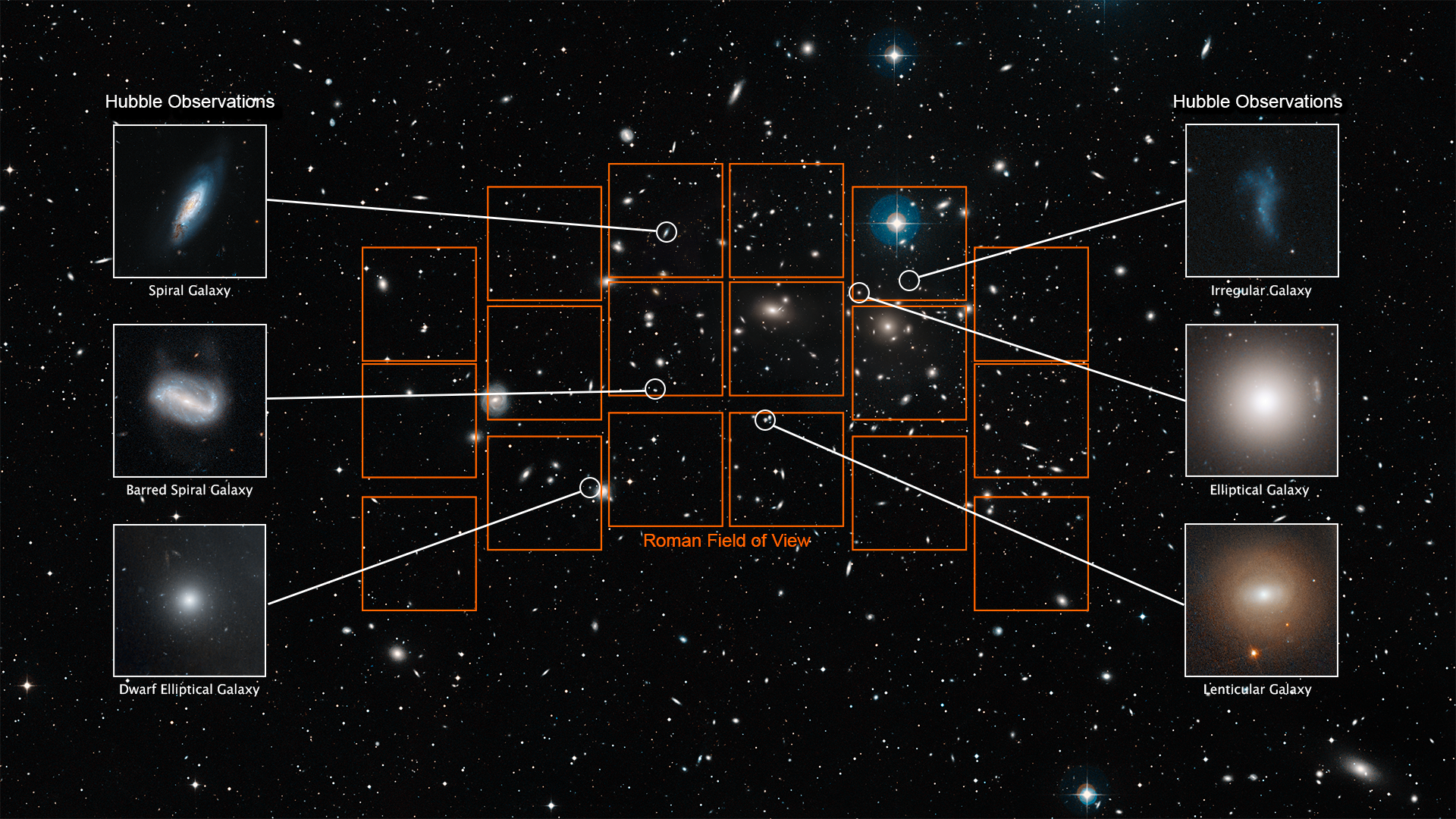
Summary of Notional Observing Programs for Prime Mission
Notional Survey | Target region | Primary spectral elements | On-sky time in notional survey plan |
|---|---|---|---|
High-Latitude Wide-Area Survey (core community survey) | Extragalactic sky, ~ 2000 deg2 | Y106, J129, H158, F184, and Grism | ~ 24 months |
High-Latitude Time-Domain Survey (core community survey) | 5-20 deg2 in the continuous field of regard,. | TBD filters + Prism | ~ 6 months |
Galactic Bulge Time-Domain (core community survey) | 2 deg2 in a low-extinction area near Galactic center | W149 filter (occasional use of other filters) | ~ 13 months |
Full sky is available | All WFI elements | ~ 15 months | |
Selected nearby stars | Coronagraph Instrument | ~ 3 months |

